Fall 2024 - P4
| Big Idea 3 | .1 | .2 | .3 | .4 | .5 | .6 | .7 | .8 | .10 |
3.2 Lesson Period 4 - Booleans Data Abstraction
Booleans - 3.2.8
Boolean in Python
A boolean in Python is a data type that can hold one of two possible values: True or False. It is often used in conditional statements to control the flow of a program. Booleans are derived from the concept of Boolean logic, which is fundamental in computer science.
Purpose
- Represent two values:
TrueandFalse, used for logical operations. - Useful for conditional statements (e.g.,
ifstatements) to control the flow of the program. - Serve as the foundation for boolean algebra and logic operations (AND, OR, NOT).
- Allow comparisons between values (e.g., checking equality, greater than, less than).
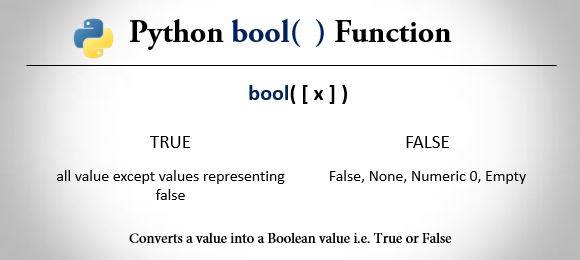
Example
# Defining boolean variables
is_active = True
is_complete = False
# Using booleans in conditional statements
if is_active:
print("The process is active.")
else:
print("The process is not active.")
```python
# Boolean Comparisons
print("print(7 <= 10):", 7 <= 10) # True
print("print(7 != 10):", 7 != 10) # True
print("print(7 == 10):", 7 == 10) # False
# Variables
num1 = 15
num2 = 30
print("\nnum1 is 15, num2 is 30")
if num1 < num2:
print("num1 is less than num2")
else:
print("num1 is not less than num2")
# Evaluating Truthiness
# Any non-empty string is considered True
# Any non-zero integer is considered True
# Empty lists and dictionaries are considered False
print("\nNon-empty string 'Python':", bool("Python")) # True
print("Zero:", bool(0)) # False
print("Non-empty dictionary {}:", bool({"key": "value"})) # True
print("Empty dictionary {}:", bool({})) # False
print(7 <= 10): True
print(7 != 10): True
print(7 == 10): False
num1 is 15, num2 is 30
num1 is less than num2
Non-empty string 'Python': True
Zero: False
Non-empty dictionary {}: True
Empty dictionary {}: False
Javascript Version
// Boolean Comparisons
console.log("console.log(7 <= 10):", 7 <= 10); // true
console.log("console.log(7 != 10):", 7 != 10); // true
console.log("console.log(7 == 10):", 7 == 10); // false
// Variables
let num1 = 15;
let num2 = 30;
console.log("\nnum1 is 15, num2 is 30");
if (num1 < num2) {
console.log("num1 is less than num2");
} else {
console.log("num1 is not less than num2");
}
// Evaluating Truthiness
// Any non-empty string is considered true
// Any non-zero integer is considered true
// Empty arrays and objects are considered false
console.log("\nNon-empty string 'JavaScript':", Boolean("JavaScript")); // true
console.log("Zero:", Boolean(0)); // false
console.log("Non-empty object {}:", Boolean({ key: "value" })); // true
console.log("Empty object {}:", Boolean({})); // false
