Fall 2024 - P4
| Big Idea 3 | .1 | .2 | .3 | .4 | .5 | .6 | .7 | .8 | .10 |
3.2 Lesson Period 4 - Sets Data Abstraction
Sets - 3.2.7
Introduction to Sets
A set in Python is an unordered collection of unique elements. Unlike lists or tuples, sets do not allow duplicates. Sets are useful when you need to eliminate duplicate items or perform mathematical operations like union, intersection, and difference.
Key Characteristics of Sets
- Sets are unordered, meaning they do not retain the order of elements.
- Elements in a set must be unique; no duplicates are allowed.
- Sets are mutable; you can add or remove elements.
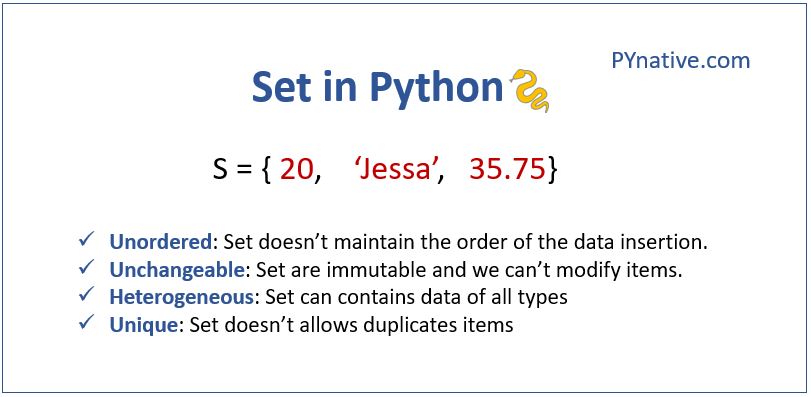
Definition of a Set
A set is defined by placing all elements (separated by commas) inside curly braces {}. You can also create a set using the set() function.
Example:
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
## Set Operations
Sets support various operations like union, intersection, and difference. Let's look at some common ones:
### 1. Adding Elements to a Set
You can add elements to a set using the `add()` method.
### Example:
```python
my_set.add(6)
print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
```python
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
my_set.add(6)
print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
2. Removing Elements from a Set
You can remove an element using the remove() method. If the element does not exist, Python will raise a KeyError.
Alternatively, use the discard() method to remove an element without raising an error if the element is not present.
Example:
my_set.remove(4)
print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 5, 6}
```python
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
# Remove an element using remove()
my_set.remove(4)
print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 5, 6}
# Remove an element using discard()
my_set.discard(7) # No error, even though 7 is not in the set
print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 5, 6}
{1, 2, 3, 5, 6}
{1, 2, 3, 5, 6}
3. Set Union
You can combine two sets using the union() method or the | operator. This returns a new set with all elements from both sets.
Example:
set_a = {1, 2, 3}
set_b = {3, 4, 5}
union_set = set_a.union(set_b) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
```python
set_a = {1, 2, 3}
set_b = {3, 4, 5}
union_set = set_a.union(set_b)
print("Union of set_a and set_b:", union_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Union of set_a and set_b: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
4. Set Intersection
The intersection() method or & operator returns a set that contains only the elements present in both sets.
Example:
intersection_set = set_a.intersection(set_b) # Output: {3}
```python
# Set Intersection
intersection_set = set_a.intersection(set_b)
print("Intersection of set_a and set_b:", intersection_set) # Output: {3}
Intersection of set_a and set_b: {3}
5. Set Difference
The difference() method returns the elements that are in one set but not in the other.
Example:
difference_set = set_a.difference(set_b) # Output: {1, 2}
```python
# Set Difference
difference_set = set_a.difference(set_b)
print("Difference between set_a and set_b:", difference_set) # Output: {1, 2}
Difference between set_a and set_b: {1, 2}
Set Hacks
Try out these challenges to test your understanding of sets!
- Create a set with the numbers
1, 2, 3, 4, 5. Add the number6and remove the number2. - Given two sets,
set_x = {10, 20, 30}andset_y = {20, 40, 60}, find their union and intersection. - How can you eliminate duplicates from the following list using a set?
my_list = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5]
# Set Hack 1: Adding and removing elements
hack_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
hack_set.add(6)
hack_set.remove(2)
print("Updated Set:", hack_set) # Output: {1, 3, 4, 5, 6}
# Set Hack 2: Union and intersection
set_x = {10, 20, 30}
set_y = {20, 40, 60}
union_xy = set_x.union(set_y)
intersection_xy = set_x.intersection(set_y)
print("Union:", union_xy) # Output: {10, 20, 30, 40, 60}
print("Intersection:", intersection_xy) # Output: {20}
# Set Hack 3: Eliminate duplicates using a set
my_list = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5]
unique_elements = set(my_list)
print("Unique elements:", unique_elements) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Updated Set: {1, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Union: {20, 40, 10, 60, 30}
Intersection: {20}
Unique elements: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Conclusion
Sets are an essential data type in Python, providing a way to handle collections of unique elements and perform common mathematical set operations. In this lesson, we explored how to create sets, add and remove elements, and perform set operations like union, intersection, and difference.
