Fall 2024 - P4
| Big Idea 3 | .1 | .2 | .3 | .4 | .5 | .6 | .7 | .8 | .10 |
3.2 Lesson Period 4 - Strings Data Abstraction
Strings - 3.2.3
Introduction to Strings
In programming, a string is a sequence of characters. Strings can include letters, numbers, symbols, and whitespace. Strings are used to represent text in a program.
Key Characteristics of Strings
- Strings are enclosed in quotes (single or double).
- They are immutable, meaning once created, they cannot be changed.
- Strings can be indexed and sliced.
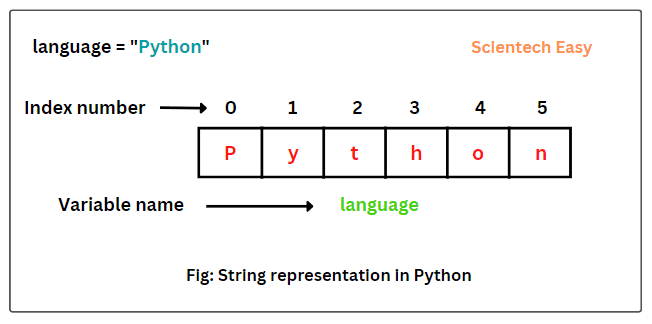
Definition of a String
A string is a data type used in programming to represent text. It is a sequence of characters, which can include letters, digits, punctuation marks, and spaces.
Example:
my_string = "I am thomas bao"
## String Operations
Strings support various operations. Here are some common ones:
### 1. String Length
You can find the length of a string using the `len()` function.
### Example:
```python
length = len(my_string)
print(length) # Output: 17
```python
# String Length
length = len(my_string)
print(length) # Output: 17
17
2. String Indexing
Strings can be accessed using indices. The first character has an index of 0.
Example:
first_character = my_string[0]
print(first_character) # Output: T
```python
# String Indexing
first_character = my_string[0]
print(first_character) # Output: T
T
3. String Slicing
You can extract a portion of a string using slicing.
Example:
substring = my_string[0:5]
print(substring) # Output: Thomas
```python
# String Slicing
substring = my_string[0:5]
print(f"Substring: {substring}") # Output: Hello
Thomas
4. String Methods
Strings come with various built-in methods. Here are a few useful ones:
lower(): Converts a string to lowercase.upper(): Converts a string to uppercase.replace(): Replaces a substring with another substring.
Example:
lower_string = my_string.lower()
print(lower_string) # Output: I am Collin.
```python
# String Methods
lower_string = my_string.lower()
upper_string = my_string.upper()
replaced_string = my_string.replace("World", "Python")
# Convert to lowercase
lower_string = my_string.lower()
print(lower_string) # Output: thomas and collin
# Convert to uppercase
upper_string = my_string.upper()
print(upper_string) # Output: THOMAS AND COLLIN
# Replace a substring
replaced_string = my_string.replace("Thomas", "Ian")
print(replaced_string) # Output: Ian and Collin
thomas and collin
THOMAS AND COLLIN
Ian and Collin
Conclusion
Strings are fundamental in programming, especially for handling text. Understanding how to manipulate strings is crucial for any programmer. In this lesson, we covered the basics of strings, including their definition, length, indexing, slicing, and some common string methods.
