3.12 Calling Procedures.
Student led teaching on Calling Procedures. Learn about how procedures and how calling allows for code reuse and modularity.
 |
Intro | .1 | .2 | .3 | .4 | .5 | .6 | .7 | .8 | .9 | .10 | .11 | .12 | .13 | .14 | .15 | .16 | .17 | .18 |
Calling Procedures:
Vocab
Procedure- A named group of programming instructions that may have parameters and return values They are referred to by different names, such as method or function, depending on the programming language
Parameter- input value of a procedure. Arguments specify the values of the parameters when a procedure is called
A Procedure call- interrupts the sequential execution of statements, causing the program to execute the statements wtithin the procedure before continuing . Once the last statement in the proceed has been executed, flow of control is returned to the point immediately following where procedure was called.
A procedure is a group of programming instructions. They’re also known as methods or functions, depending on the programming language. You can use a procedure to use the same set of instructions, again and again, without having to rewrite it into your code.In AP Pseudocode, here’s how they’ll represent procedures: 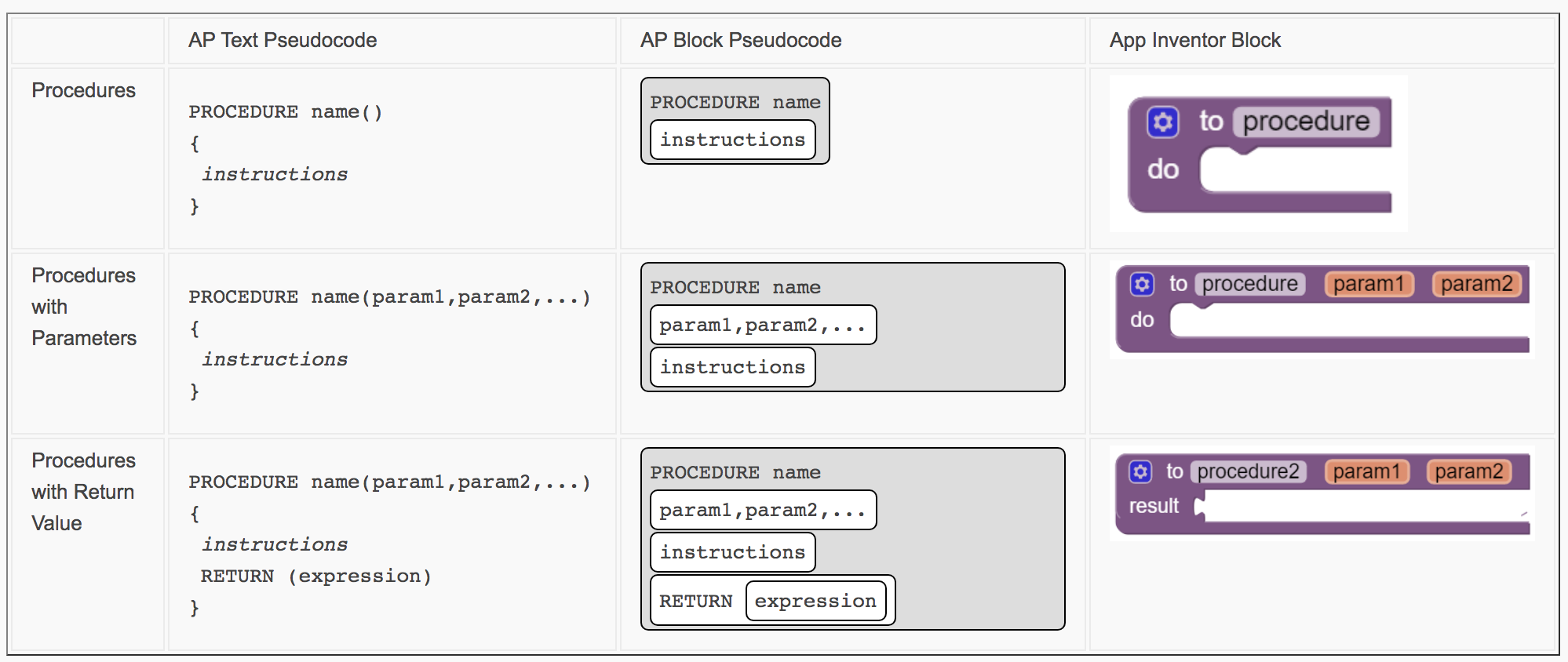
first_number = 5
second_number = 7
sum_value = first_number + second_number
print (sum_value)
It goes without saying that, if you wanted to sum more than one set of numbers at a time, you’d have to rewrite these lines over and over again…
Let’s see how we’d go about writing this as a function, or a procedure in Python.
A function in Python looks like this:
def name_of_function (parameter1, parameter2):
#code statements here
So our summing machine would look like this!
def summing_machine(first_number, second_number):
print (first_number + second_number)
When you call a procedure, your program acts like those lines of code are written out. Once it’s done executing those code lines, your program goes back to reading code sequentially.
When you call that procedure with defined values or variables, those values are known as arguments.
def summing_machine(first_number, second_number):
print (first_number + second_number)
summing_machine(5, 7)
#In this example, 5 and 7 are examples of arguments.
For example:
def summing_machine(first_number, second_number):
value = first_number + second_number
return (value)
answer = summing_machine(5, 7)
print (answer)
#you can use this to manipulate the value the function returns as well.
print (answer + 1)
LETS LOOK AT AN EXAMPLE:
In this example this is a simple procedure to create a code for calculating the area
# Define the calculate_area procedure
def calculate_area(length, width):
# Calculate the area here
area = length * width
return area
# Call the procedure with different values
length1 = 5
width1 = 3
area1 = calculate_area(length1, width1)
# Print the results
print(f"The area of the first rectangle is {area1}")
The area of the first rectangle is 15
Hacks
Review the following and complete
- Code a procedure that finds the square root of any given number and call it to find the square root of 64
- The following questions from Collegeboard:
Quiz:
1 In Python, what can be done by a value returned by a procedure?
a. Define input variables for another procedure
b. Print it to console
c. Call another procedure with it
d. Assign it to a variable or use it in expressions
2. When a Procedure is called, what happens to the programs execution?
a. it prints the result of the procedure
b. it exits the program and terminates execution
c. it moves to the next line of code in the program
d. it acts as if the lines of code on the procedure are written out
3 Which of the following is an example of a procedural call in Python?
a. def summing_machine(first_number, second_number)
b. summing_machine(5, 7)
c. print(first_number + second_number)
d. return(value)
firstnum = 1
secondnum = 2
thirdnum = 3
fourthnum = 4
print(firstnum)
1
12
10
12
12
10
12
Multiplication Table for 5 (Up to 10):
5 x 1 = 5
5 x 2 = 10
5 x 3 = 15
5 x 4 = 20
5 x 5 = 25
5 x 6 = 30
5 x 7 = 35
5 x 8 = 40
5 x 9 = 45
5 x 10 = 50