3.11 Search
Student led teaching on Search. Learn about searches, such as binary search and how they vary in efficiency and the way they work.
 |
Intro | .1 | .2 | .3 | .4 | .5 | .6 | .7 | .8 | .9 | .10 | .11 | .12 | .13 | .14 | .15 | .16 | .17 | .18 |
Search
A search algorithm is an algorithm that retrieves information stored in a data structure or calculated in the search space of a problem domain, with either discrete or continuous values.
Linear Search
The most basic way of searching in which each element is searched in the order it appears in the list. The list doesn’t need to be organized.
For the code given below, the algorithm compares each value to the previous value, and if the value is smaller than the previous value, that value becomes the new min. The algorithm continues until it reaches the end of the list. This should be similar to the hack you did from Lists (idea 3.10)!
nums[] ← [86, 75, 98, 100, 71, 65, 84]
min ← nums[0]
FOR EACH score IN nums[] DO
IF score < min THEN
min ← score
END IF
END FOR
OUTPUT "The minimum value in the list is:", min
Python Code
nums = [86, 75, 98, 100, 71, 65, 84]
print(nums)
min = nums[0]
for score in nums:
if (score < min):
min = score
print("The minimum value in the list is:", min)
[86, 75, 98, 100, 71, 65, 84]
The minimum value in the list is: 65
Binary Search
A binary search, also known as half-interval search, logarithmic search, or binary chop is a search algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array.
- Binary Search is a method of searching for an element in a list.
- Binary Search is faster than Linear Search
-
Binary search works on sorted arrays.
-
Binary search begins by comparing an element in the middle of the array with the target value.
-
If the target value matches the element:
- Its position in the array is returned and exit the program.
-
If the target value is less than the element:
- The search continues in the lower half of the array. Go to Step-2
-
If the target value is greater than the element, the search continues in the upper half of the array. Go to Step-2
-
Go back to Step-2
-
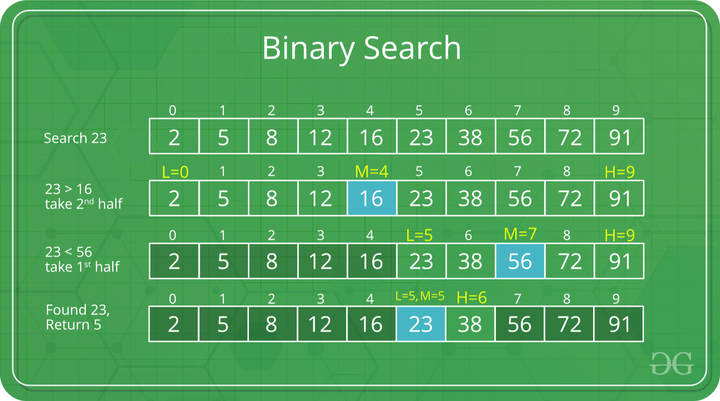
- Worst Case Scenario: 4 Iterations
# Returns index of x in arr if present, else -1
def binary_search(arr, low, high, x):
# Check base case
if high >= low:
mid = (high + low) // 2
# If element is present at the middle itself
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If element is smaller than mid, then it can only
# be present in left subarray
elif arr[mid] > x:
return binary_search(arr, low, mid - 1, x)
# Else the element can only be present in right subarray
else:
return binary_search(arr, mid + 1, high, x)
else:
# Element is not present in the array
return -1
# Test array
arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]
x = 10
# Function call
result = binary_search(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print("The Element is in index", str(result))
else:
print("Element is not present in array")
The Element is in index 3
Big O Notation
Usually used to denote how much run time an algorithm takes or how much memory is used by an algorithm.
In our case we are using it to show how many tries it will take for a search algorithm to find something.
Linear Search vs Binary Search big O notation:
- Linear search complexity is denoted by O(n) as every element in the array is compared only once.
- In linear search, best-case complexity is O(1) where the element is found at the first index.
- Worst-case complexity is O(n) where the element is found at the last index or the element is not present in the array.
- Binary search, best-case complexity is O(1) where the element is found at the middle index. The worst-case complexity is O(log base 2 n).
Hacks
Review each of the following and produce….
- A binary search algorithm that sorts for the value 25.
- nums = [12, 23, 25, 45, 47, 89, 91]
- A python function that can determine the worst case number of iterations of a binary search for an array of length 20.