 |
Graph Theory | Java Graphs | Searching |
Graph Heuristics - Breadth First Search and Depth First Search
Categories: Java SpringSearching
Problem: Given a starting node, I want to find a path to the end node.
Popcorn Hack #3
As a human, how might you do this? Describe a process.
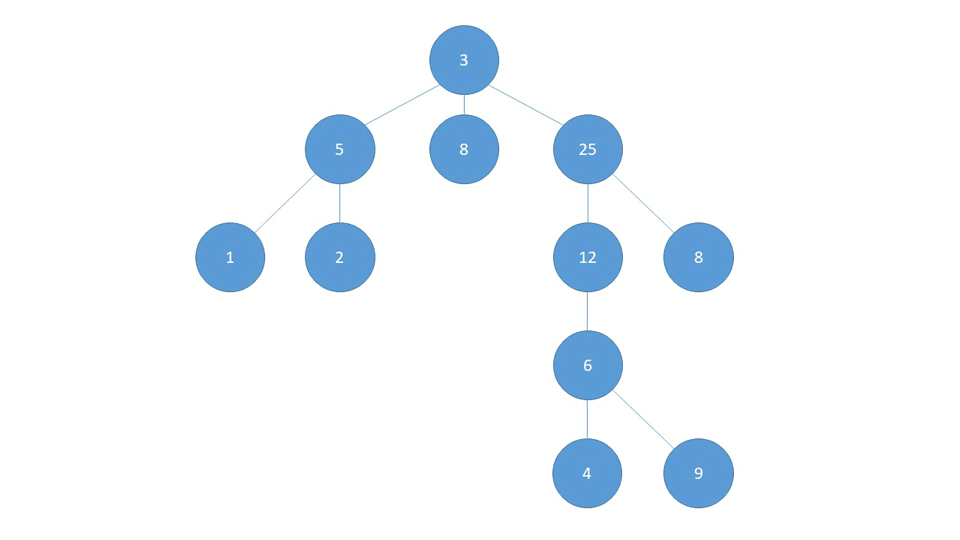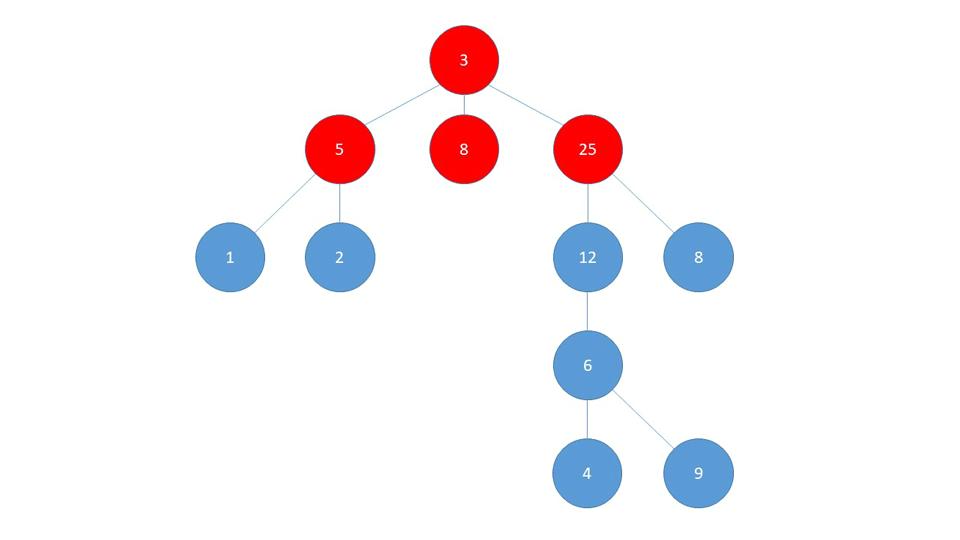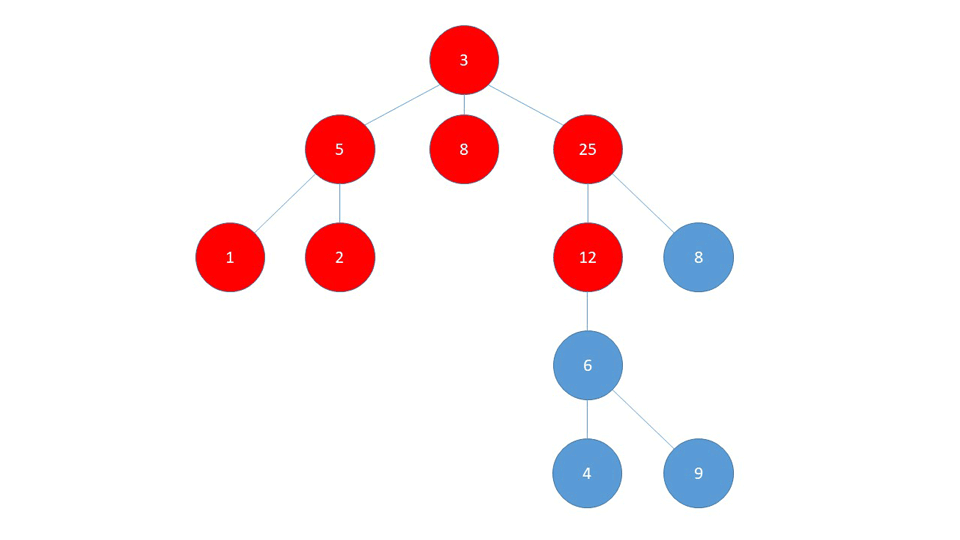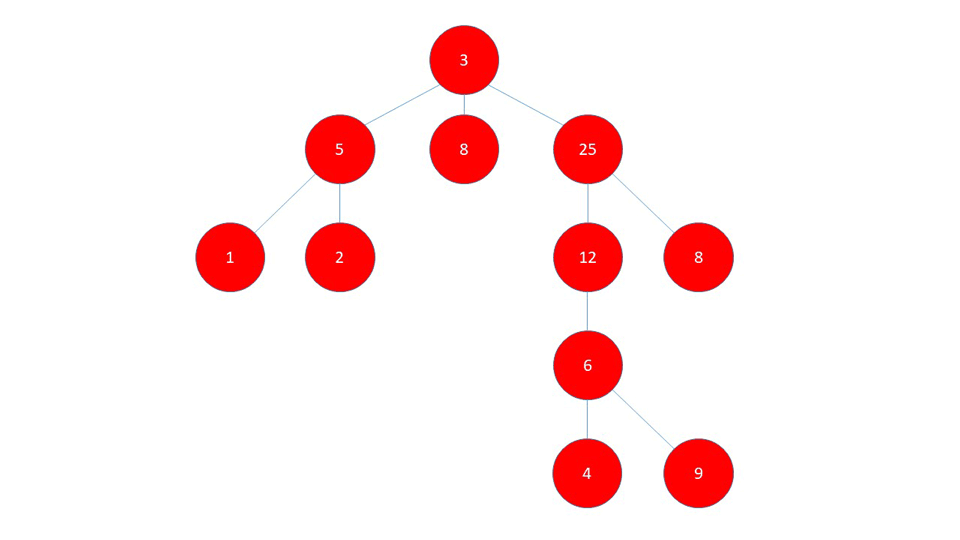
BFS
- Check if the starting node is equal to target
- Move to every node connected to starting node
- Check if each of those nodes are equal to the target
- Move to every node connected to one you just checked
- Check if each of those nodes are equal to the target
- Repeat
BFS first checks the nodes closest to the starting node, and checks the nodes farthest away last.
import java.util.*;
public class Graph {
private int nodes;
private LinkedList<Integer>[] adjacencyList;
public Graph(int nodes) {
this.nodes = nodes;
adjacencyList = new LinkedList[nodes];
for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++) {
adjacencyList[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
}
public void addEdge(int source, int destination) {
adjacencyList[source].add(destination);
}
public void displayGraph() {
System.out.println("Graph adjacency list:");
for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++) {
System.out.print(i + " -> ");
for (int neighbor : adjacencyList[i]) {
System.out.print(neighbor + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void bfs(int start, int target) {
// queue is used to explore nodes in breadth-first order
// essentially, any encountered nodes are added to the Queue
// Queue is then iterated in order to see who to visit next
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// tracks each node's parent to reconstruct the path
Map<Integer, Integer> parent = new HashMap<>();
queue.add(start);
// start node has no parent
parent.put(start, -1);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int current = queue.poll();
System.out.println("Visiting: " + current);
if (current == target) {
System.out.println("Target " + target + " found!");
printPath(parent, target);
return;
}
for (int neighbor : adjacencyList[current]) {
// track how neighbor was reached
parent.put(neighbor, current);
// add neighbor to queue; means will visit at some later point
queue.add(neighbor);
}
}
System.out.println("Target " + target + " not found.");
}
private void printPath(Map<Integer, Integer> parent, int target) {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
for (int at = target; at != -1; at = parent.get(at)) {
path.add(at);
}
Collections.reverse(path);
System.out.println("Path: " + path);
}
}
// Sample Usage
Graph graph = new Graph(7);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 3);
graph.addEdge(1, 4);
graph.addEdge(2, 5);
graph.addEdge(3, 6);
graph.displayGraph();
System.out.println("");
graph.bfs(0, 6);
Graph adjacency list:
0 -> 1 2
1 -> 3 4
2 -> 5
3 -> 6
4 ->
5 ->
6 ->
Visiting: 0
Visiting: 1
Visiting: 2
Visiting: 3
Visiting: 4
Visiting: 5
Visiting: 6
Target 6 found!
Path: [0, 1, 3, 6]
DFS
- Check if the starting node is equal to target
- Move to the first node connected to the target
- Check if that node is equal to the target
- Move to the first node connected to the node in 2
- Check if that node is equal to the target
- Repeat 2-3 until there are no more child nodes
- Backtrack a Node
- Repeat 4-5
- Repeat 2-6
DFS first checks every node in a “branch” of the tree, before moving on the next branch
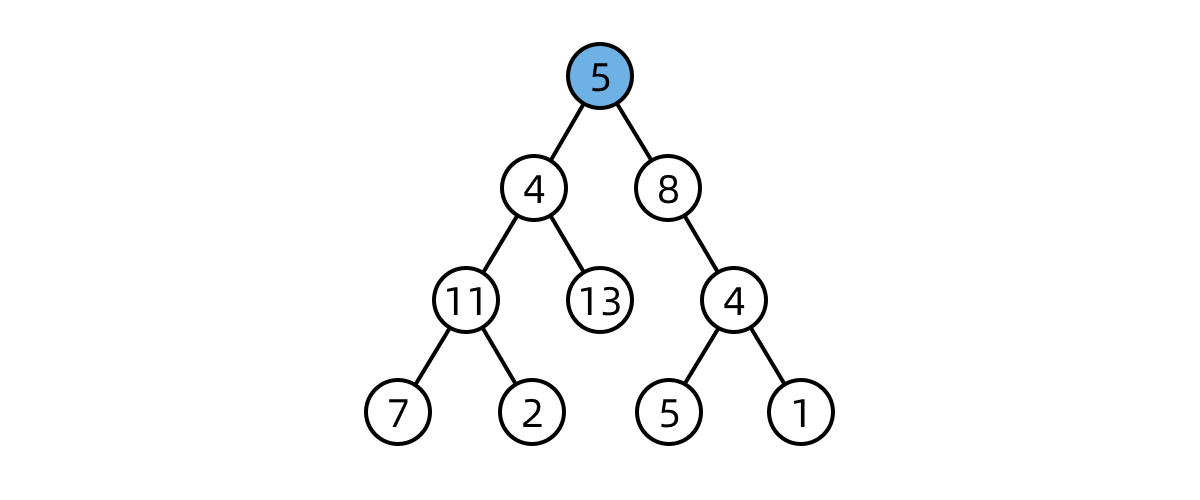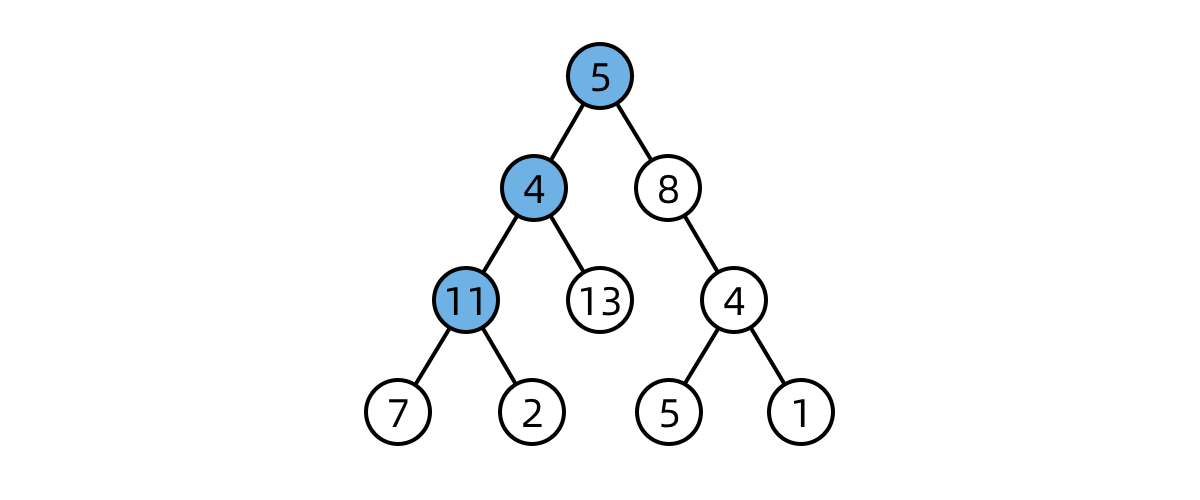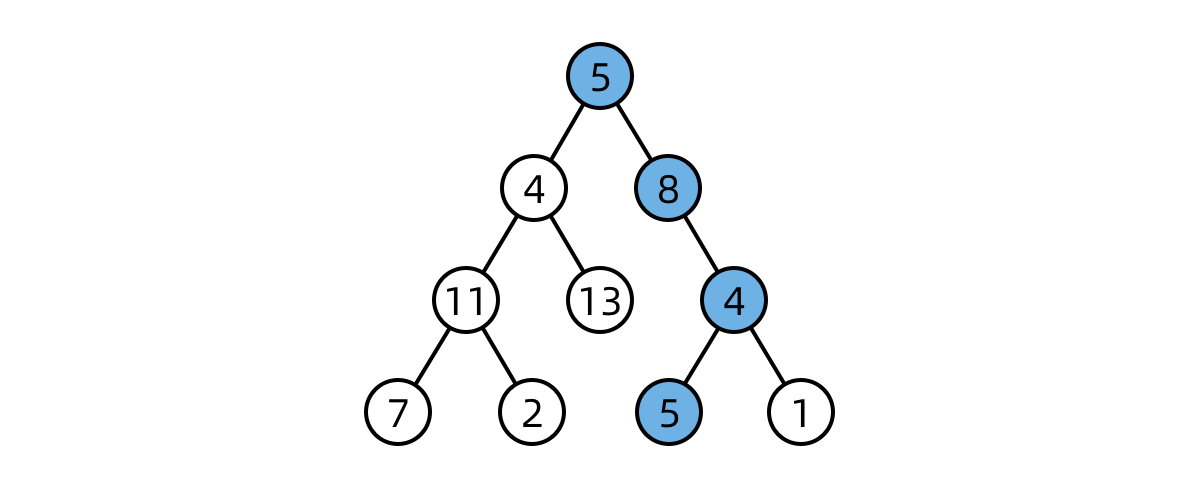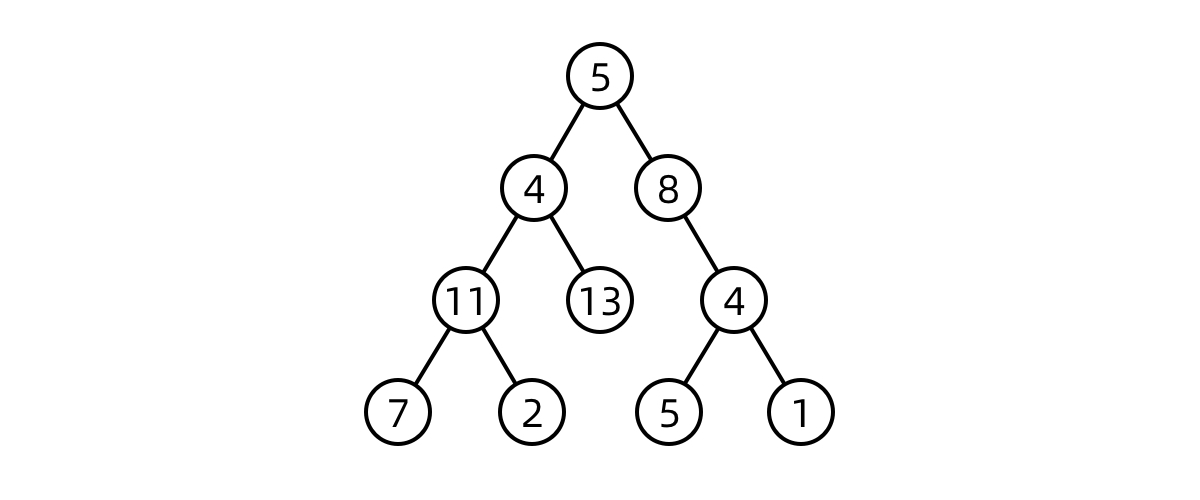
import java.util.*;
public class Graph {
private int nodes;
private LinkedList<Integer>[] adjacencyList;
public Graph(int nodes) {
this.nodes = nodes;
adjacencyList = new LinkedList[nodes];
for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++) {
adjacencyList[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
}
public void addEdge(int source, int destination) {
adjacencyList[source].add(destination);
}
public void displayGraph() {
System.out.println("Graph adjacency list:");
for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++) {
System.out.print(i + " -> ");
for (int neighbor : adjacencyList[i]) {
System.out.print(neighbor + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void bfs(int start, int target) {
// queue is used to explore nodes in breadth-first order
// essentially, any encountered nodes are added to the Queue
// Queue is then iterated in order to see who to visit next
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// tracks each node's parent to reconstruct the path
Map<Integer, Integer> parent = new HashMap<>();
queue.add(start);
// start node has no parent
parent.put(start, -1);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int current = queue.poll();
System.out.println("Visiting: " + current);
if (current == target) {
System.out.println("Target " + target + " found!");
printPath(parent, target);
return;
}
for (int neighbor : adjacencyList[current]) {
// track how neighbor was reached
parent.put(neighbor, current);
// add neighbor to queue; means will visit at some later point
queue.add(neighbor);
}
}
System.out.println("Target " + target + " not found.");
}
public void dfs(int start, int target) {
// tracks the parent of each visited node
Map<Integer, Integer> parent = new HashMap<>();
dfsHelper(start, target, parent);
}
private boolean dfsHelper(int current, int target, Map<Integer, Integer> parent) {
System.out.println("Visiting: " + current);
if (current == target) {
System.out.println("Target " + target + " found!");
printPath(parent, target);
return true;
}
for (int neighbor : adjacencyList[current]) {
// track how we reached this neighbor
parent.put(neighbor, current);
if (dfsHelper(neighbor, target, parent)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void printPath(Map<Integer, Integer> parent, int target) {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
for (int at = target; at != -1; at = parent.get(at)) {
path.add(at);
}
Collections.reverse(path);
System.out.println("Path: " + path);
}
}
// Sample Usage
Graph graph = new Graph(7);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 3);
graph.addEdge(1, 4);
graph.addEdge(2, 5);
graph.addEdge(3, 6);
graph.displayGraph();
System.out.println("");
graph.dfs(0, 6);
Graph adjacency list:
0 -> 1 2
1 -> 3 4
2 -> 5
3 -> 6
4 ->
5 ->
6 ->
Visiting: 0
Visiting: 1
Visiting: 3
Visiting: 6
Target 6 found!
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
java.lang.NullPointerException: Cannot invoke "java.lang.Integer.intValue()" because the return value of "java.util.Map.get(Object)" is null
at Graph.printPath(#12:1)
at Graph.dfsHelper(#12:1)
at Graph.dfsHelper(#12:1)
at Graph.dfsHelper(#12:1)
at Graph.dfsHelper(#12:1)
at Graph.dfs(#12:1)
at .(#48:1)
Homework - Part 3
- What happens if the graph has a loop in it? Please account for this in the two algorithms above.
BONUS:
- Traveling Salesman but cursed
- Your code should take in a graph and output the fastest path to travel to every single graph given a starting and ending node
- Assume each edge has the same cost
- Efficiency doesn’t matter
