BI 2 | Data | Binary Logic
This is a mini project, warming up to CPT guidelines. Read this to article and starrt developing ideas for your Binary Logic requirements. Real binary abstractions include ASCII, Unicode, RGB Colors, Images,Logic Gates, etc.
- Introduction
- Binary Calculator
- Math in Binary
- Understand binary digits in Numbers (2^^0, 2^^1, 2^^2)
- ASCII and Unicode
- Color Codes
- Logic Gates
Introduction
Algorithms, Data, Data Structures, and Visualization can go together. This blog is a collection of binary, data and data structures and could be a great CPT practice project, if combined with visualization.
Binary Calculator
Obtain code form teacher_portfolio project.
This UI helps illustrate binary and decimal. Often, the learn concepts, it is best to code an example to help understand what is happening.
-
Tour Binary Frontend Code* to get you started.
-
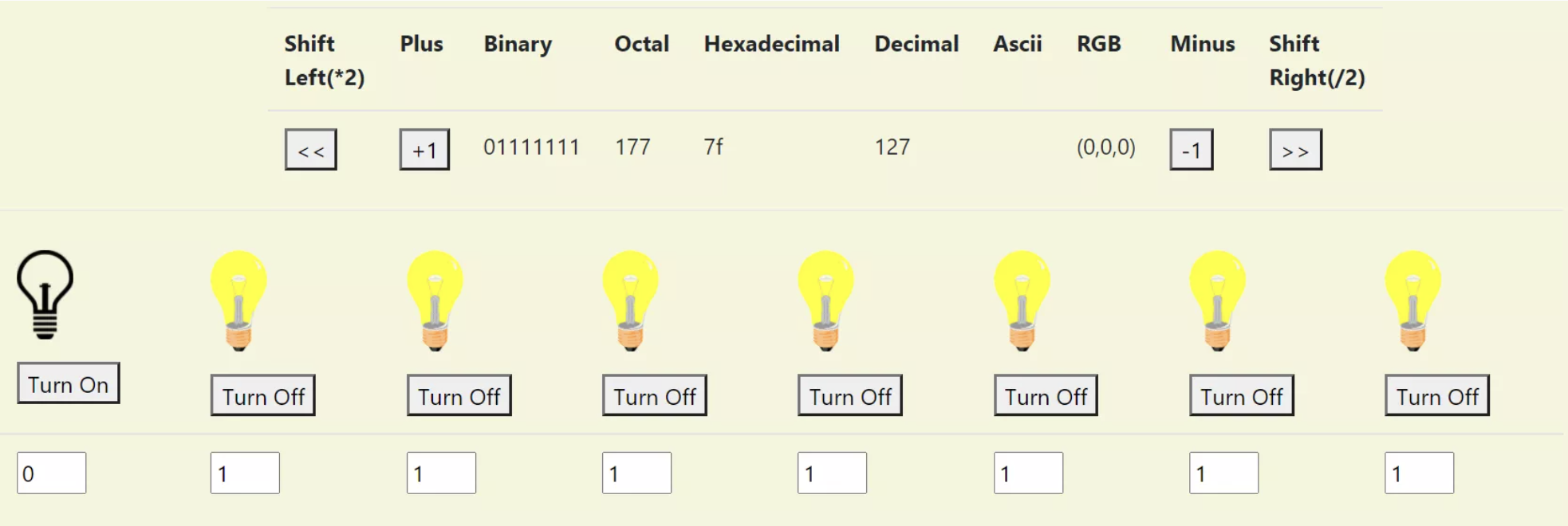
Make a new operation in the Calculator called Shift
- Right Shifts (divides by 2^n)
- Left Shifts (multiplies by 2^n)
- Add buttons for “«” and “ »”
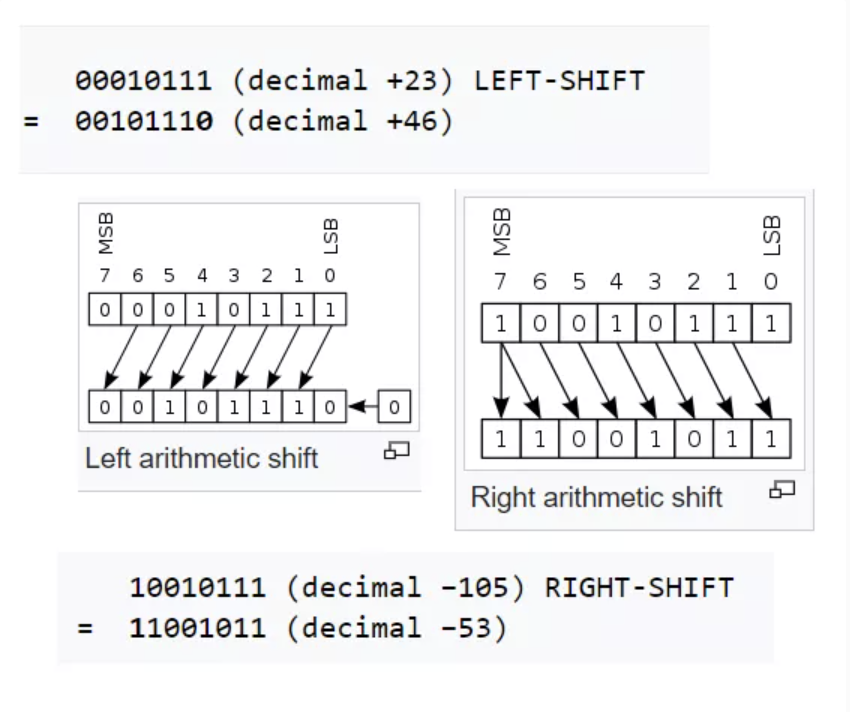
- In an arithmetic shift, the bits that are shifted out of view are discarded
Math in Binary
Learn binary, bitwise operators, and more.
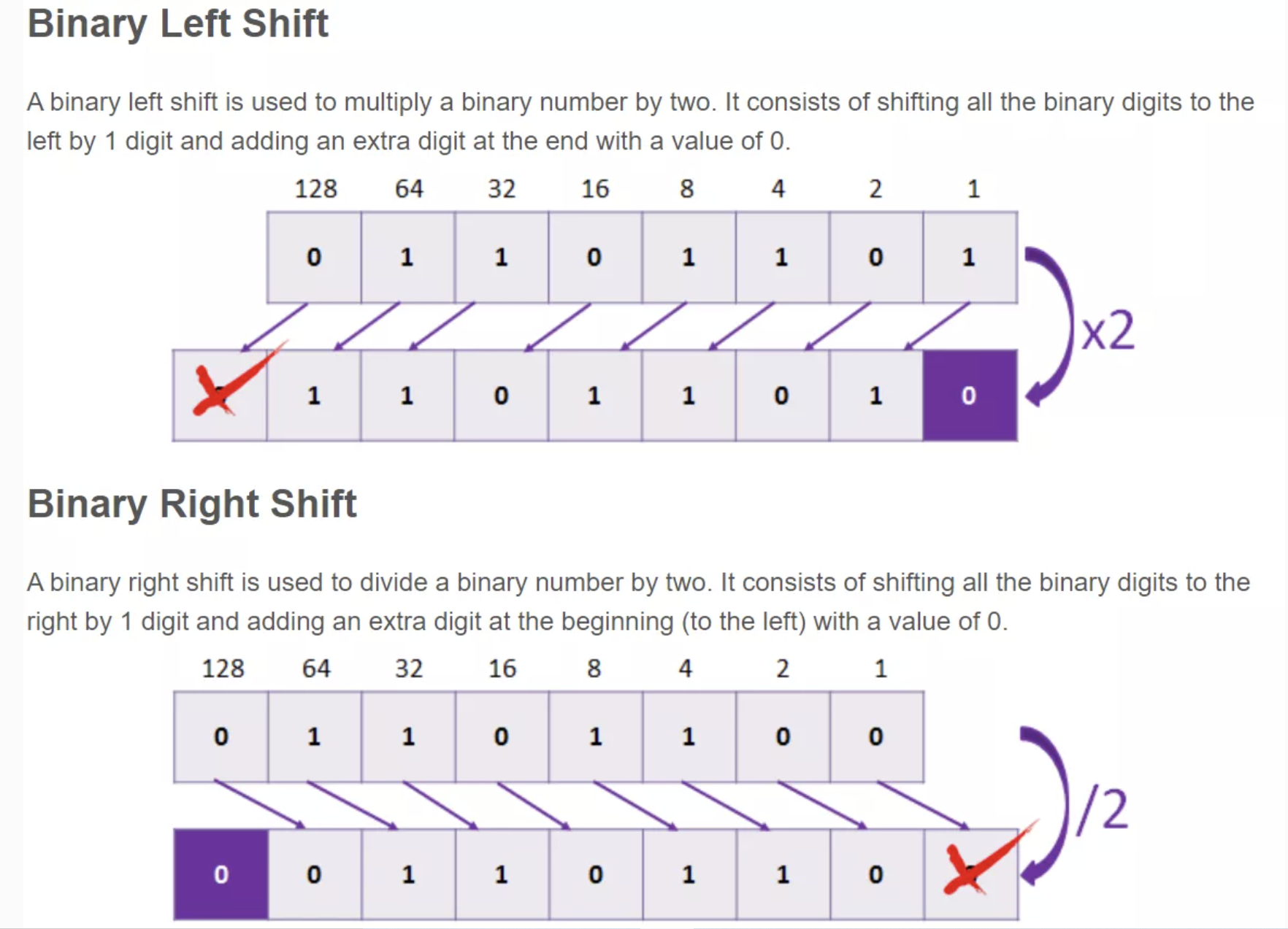
- Shifting bits is a common computer operation and does wonderful things in math like multiply and divide.
- Least Significant Bit (SB) always determines if binary numbers is odd or even.
- Look for shift on w3schools
Understand binary digits in Numbers (2^^0, 2^^1, 2^^2)
How does the Power of 2 work? What is a binary number? What is Base2, Base10, Base16.
- This example uses an 8-bit register. Math can be represented in much in many more bits, 32 bits or 2 bytes is common for integer in modern computer languages.
- Most Significant Bit (MSB). This example shows negative and positive numbers, using technique called Twos Complement.
ASCII and Unicode
Computers represent more than Math. Mostly everyone is familiar with the characters on a keyboard and Emojis. These are all represented in binary, the data abstraction being the characters we visualize. 😂
Character Data Abstraction
How are characters stored? How many bits do they take?
- ASCII is 8 bits, it generally represent keys on keyboard. Look up ASCII Table.
- Unicode can be UTF-8, 16 or 32, each representing bits. ASCII is preserved in Unicode.
- ASCII - 7 bits, extended to 8 bits with Unicode
- UTF-8
- UTF-16
- UTF-32
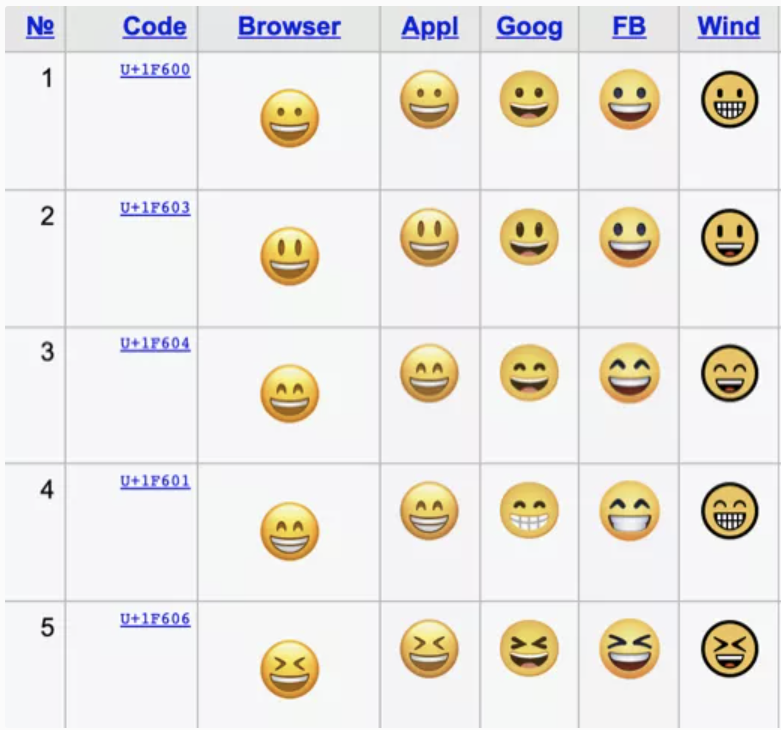 Sample of Unicode characters.
Sample of Unicode characters.
Character Concept/Design
The ASCII value in picture should be changed based off of the bits in evaluation you are doing. Bits displayed, label, and evaluation would be specific to evaluation type:
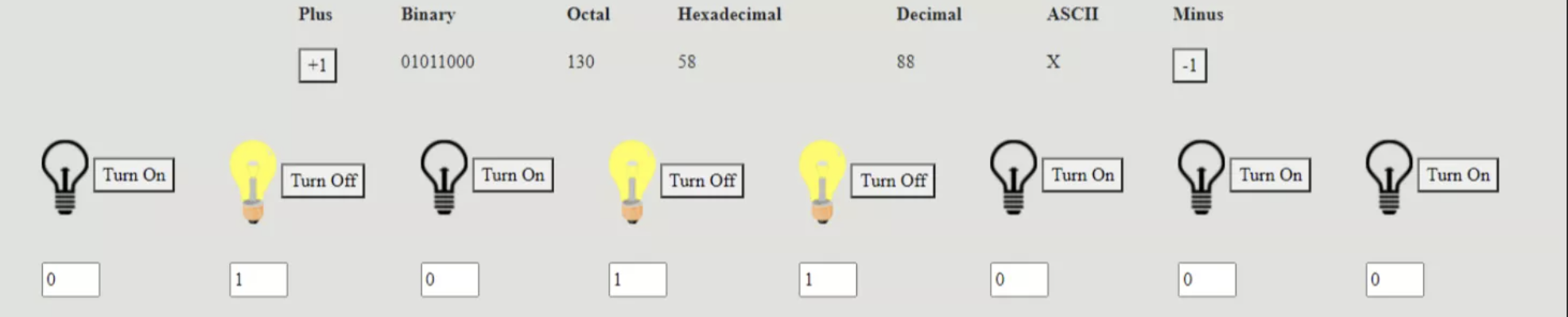 Original ASCII
Original ASCII
Color Codes
Pixels are little dots on Monitors and TVs that make up the display. Each pixel has an Red Green and Blue value (RGB). All pictures we see or take are composed of RGB using a density measurement. These are stored and then represented by digitally or in print.
- Monitors
- 1280 x 1024 Super-eXtended Graphics Array (SXGA)
- 1366 x 768 High Definition (HD)
- 1600 x 900 High Definition Plus (HD+)
- 1920 x 1080 Full High Definition (FHD)
- 1920 x 1200 Wide Ultra Extended Graphics Array (WUXGA)
- TVs
- 4K Ultra HD: The term 4K means the screen is about 4,000 pixels wide. …
- 1080p (Full HD): This resolution is 1,920 x 1,080 pixels. …
- 720p (HD Ready): This is mostly found on smaller TVs, and it has a resolution of 1,280 x 720.
- Camera |Sensor Resolution (megapixels)|Typical Image Resolution (pixels)| |2.16|1800 x 1200| |3.9|2272 x 1704| |5.0|2592 x 1944| |7.1|3072 x 2304| |8.0|3264 x 2448| |10.0|3648 x 2736| |12.1|4000 x 3000| |14.7|4416 x 3312| |21.0|5616 x 3744|
A Color code is a 24 bit abstraction
There are 8 bits for Red, 8 bits for Blue, and 8 bits for Green.
| Name | Hex Code | RGB Code |
| Black | #000000 | rgb(0, 0, 0) |
| Red | #FF0000 | rgb(255, 0, 0) |
| Maroon | #800000 | rgb(128, 0, 0) |
| Yellow | #FFFF00 | rgb(255, 255, 0) |
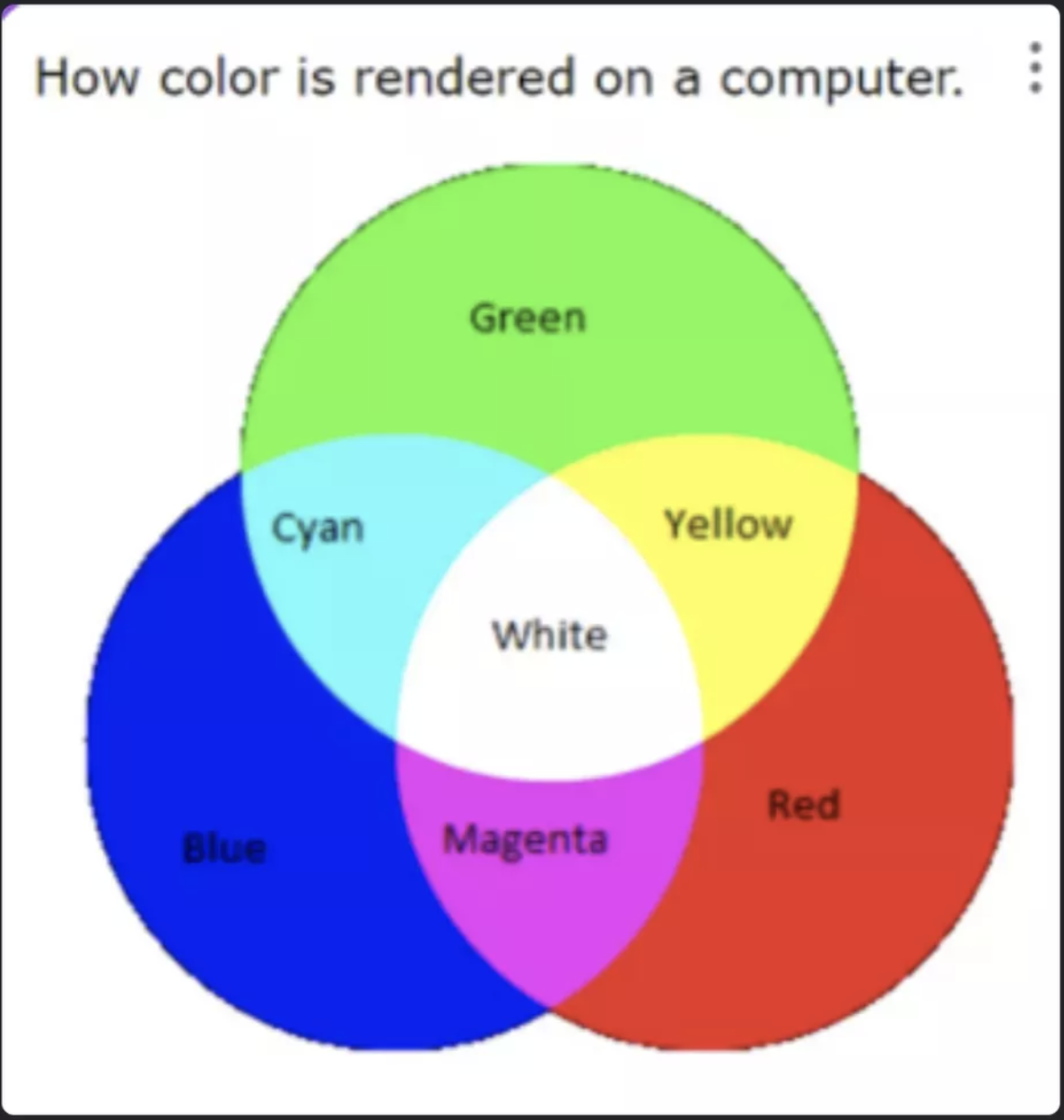 255 * 255 * 255 combinations of R, G, B
255 * 255 * 255 combinations of R, G, B
Color UI Design
Here is a sample program a student used to visualize color by turning buttons on and off.
by Anthony Vo 3 rows representing R, G, B Resulting color displayed in block
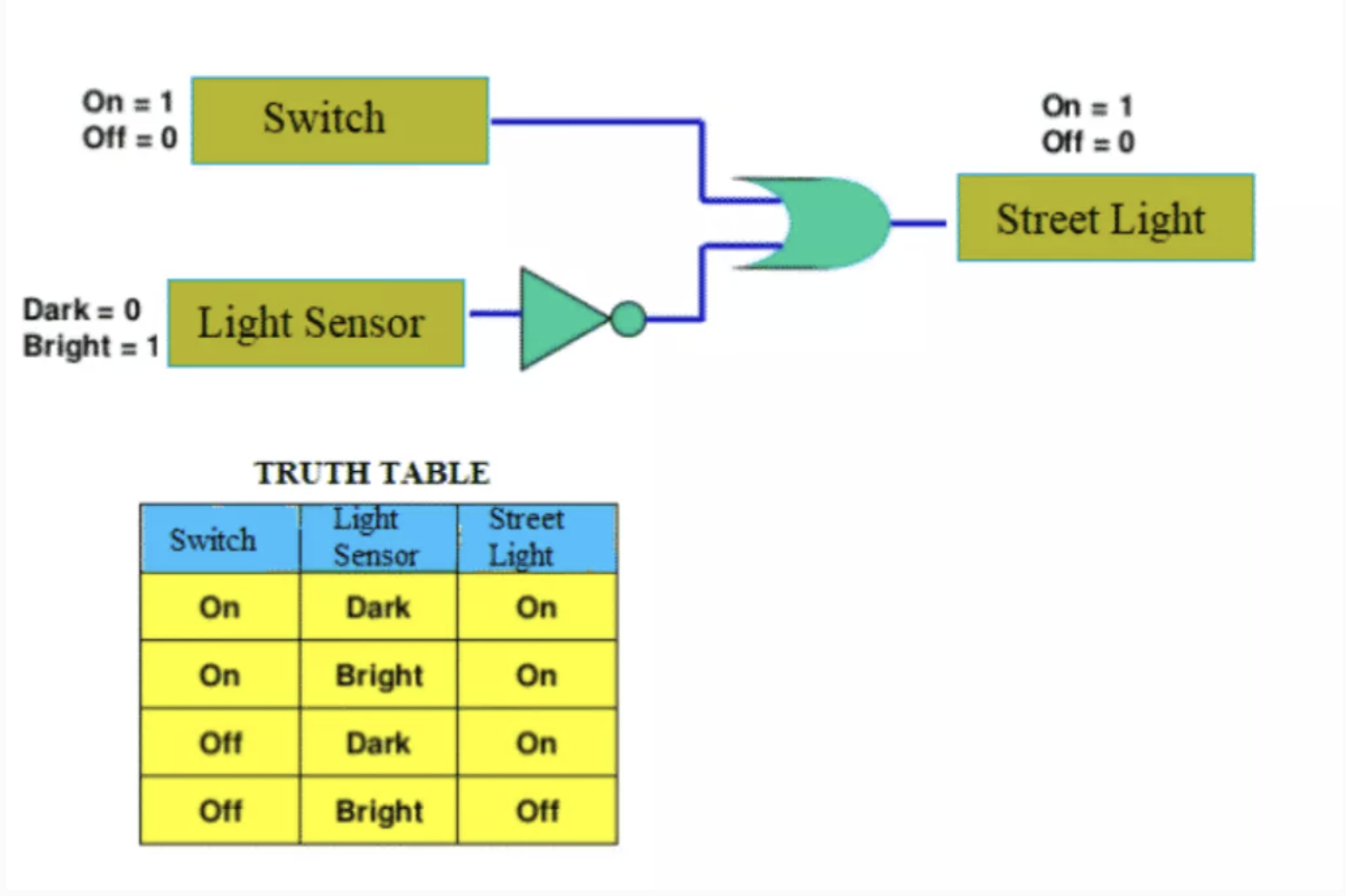
Logic Gates
The fundamentals of all decisions in computers is made by logic gates. These gates are visualized by permuting 1 and 0 across many different types of decisions. The result is an expression that evaluated to 1 or 0. These are called Truth Tables.
Logic Gates can be simulated with 2 bits
Look for bitwise operators on w3schools
Logic UI Concept
Visual concept of logic gates
- Establish check boxes for A / B on and off
- Show result of Boolean Expression using Gate visual
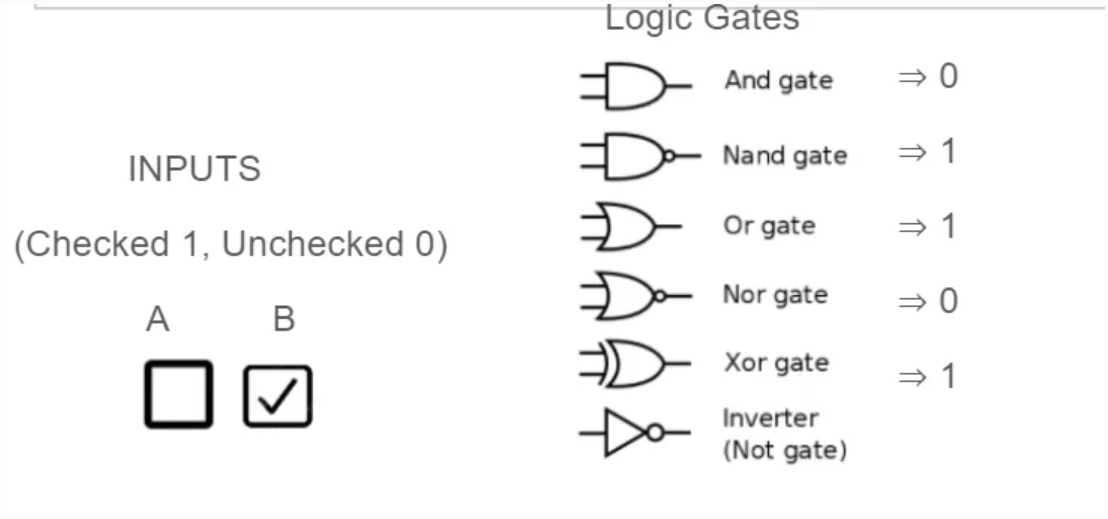 Logic Gates
Logic Gates
Logic UI Design
Logic gate lab in JavaScript
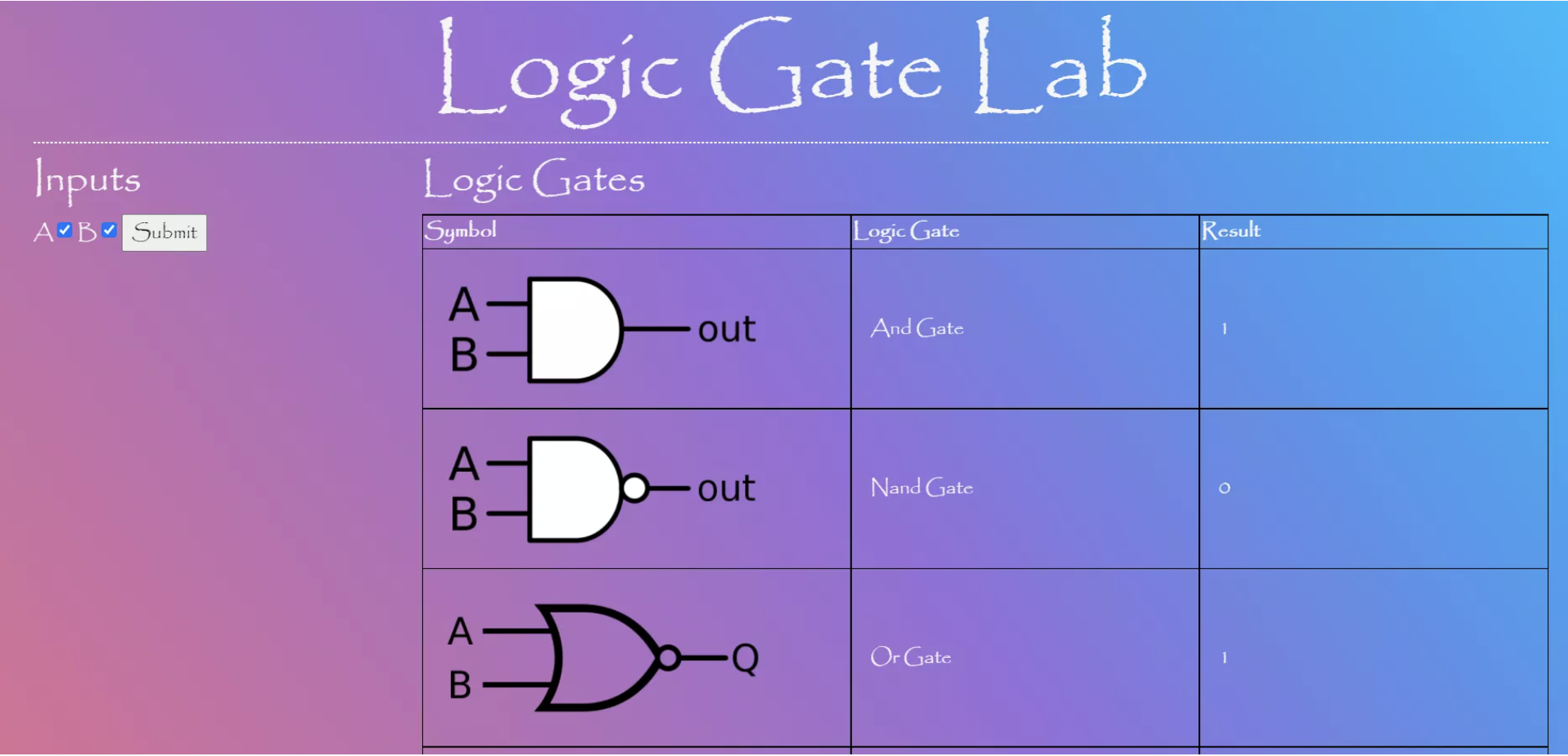 by Kylie Scharf
AB checkboxes with Submit button
Table with Symbol, Description, and Result
by Kylie Scharf
AB checkboxes with Submit button
Table with Symbol, Description, and Result
Logic of Logic Gates
A logic gate can have two inputs (a,b) and by how changing these inputs it impacts the output(c).
- There are four possible inputs:
- 0 0
- 0 1
- 1 0
- 1 1
- Understanding the output enables us to understand a logical expressions. All outputs are routed in Logic Gates (similar to how a language is routed in Latin).
- AND is true for 1 1; NAND is true opposite of AND 0 0, 0 1, 1 0
- OR is true for 1 1, 0 1, 1 0, NOR is true opposite of OR 0 0
- XOR is true for 0 1, 1 0
Practical Application
Logic gates are used everywhere