Sorting Algorithms
Working with Data Structures and manipulating data.
import random
numbers = []
for i in range(10):
numbers.append(random.randint(0,100))
print("Random List")
print(numbers)
Explore
Get into groups of 3
We will be focusing on 4 algorithms today.
We will look at the first one together, Bubble Sort
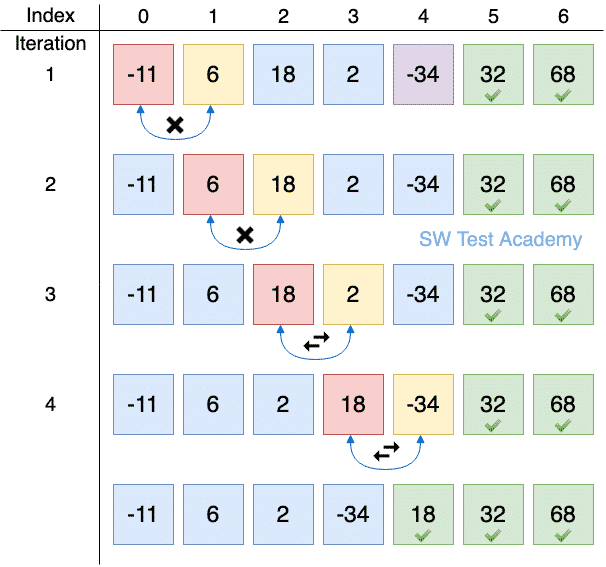
What is happening with this sort?
In your groups you will each choose to be an expert on a sorting algorithm. Merge, Selection, and Insertion. Take about 5 minutes to read about your algorithm (Geek for Geeks linked below) and be ready to explain it to your other group members.
import nltk
import random
from nltk.corpus import words
nltk.download('words') # Download the word list (only required once)
english_words = words.words()
def new_words():
# You can now use the 'english_words' list in your code
random_words = []
for i in range(10):
random_words.append(english_words[random.randint(0,len(english_words))])
return random_words
print("Random List")
print(new_words())
words = new_words()
print(words)
def bubbleSort(list):
n = len(list) - 1 # list are indexed 0 to n-1, len is n
# Traverse through list with i index
for i in range(n):
swapped = False # optimize code, so it exits if now swaps on inner loop
# Inner traversal using j index
for j in range(n-i): # n-i as positions on right are in order in bubble
# Swap if the element KeyN is greater KeyN1
keyN = list[j]
keyN1 = list[j+1]
if keyN > keyN1:
swapped = True
list[j], list[j + 1] = list[j + 1], list[j] # single line swap
if not swapped: # if no swaps on inner pass, list is sorted
return # exit function
bubbleSort(words)
print(words)
words = new_words()
print(words)
def selectionSort(list):
n = len(list) # length is n
# List is traversed from index 0 to n-1, n elements
for i in range(n):
smallI = i # small index is captured
smallV = list[i]
# Inner traversal looks at elements after i
for j in range(i+1, n):
# Save reference if less
keyV = list[j]
if keyV < smallV:
smallI = j # small index is replaced
smallV = keyV
# swap smallest to current i positon, sorting left to right
list[i], list[smallI] = list[smallI], list[i] # single line swap
selectionSort(words)
print(words)
Discuss
Answer the following with your group.
- When should you use each algorithm? What makes an algorithm the right choice?
- Given the following lists...
- [0, 2, 6, 4, 8, 10]
- [Elephant, Banana, Cat, Dog, Apple]
- [29, 13, 83, 47, 32, 78, 100, 60, 65, 15, 24, 9, 40, 68, 53, 8, 90, 58, 39, 32, 34, 91, 74, 94, 49, 87, 34, 87, 23, 17, 27, 2, 38, 58, 84, 15, 9, 46, 74, 40, 44, 8, 55, 28, 81, 92, 81, 88, 53, 38, 19, 21, 9, 54, 21, 67, 3, 41, 3, 74, 13, 71, 70, 45, 5, 36, 80, 64, 97, 86, 73, 74, 94, 79, 49, 32, 20, 68, 64, 69, 1, 77, 31, 56, 100, 80, 48, 75, 85, 93, 67, 57, 26, 56, 43, 53, 59, 28, 67, 50] Select the algorithm you believe is best for each, explain.
HACKS
Provided below is a Bubble Sort Algorithm sorting a list of dictionaries based off of selected key.
-
Now it's time to do some coding...
-
Run code and then research and answer these questions...
- Is a list and/or dictionary in python considered a primitive or collection type? Why?
- Is the list passed into bubble sort "pass-by-value" or "pass-by-reference? Describe why in relation to output.
-
Implement new cell(s) and/or organize cells to do the following.
- Create your own list
- Use your expertise sorting algorithm (selection, insertion, merge). Note, I got my bubble sort from Geek for Geeks and made modifications. Each student in a group should have a unique algorithm.
- Test your list with my bubble sort
- Test my list with your new sort
- Research analysis on sorting:comparisons, swaps, time. Build this into your hacks. - Find a better way to print the data, key first, then other elements in viewable form.
Use the code below to help guide your adventure
"""
* Creator: Nighthawk Coding Society
Bubble Sort of a List of Dictionaries with optimizations, every key in row 0 is used to sort and resort list.
"""
# bubble sorts a list of dictionaries, base off of provided key
def bubbleSort(list, key):
n = len(list) - 1 # list are indexed 0 to n-1, len is n
# Traverse through list with i index
for i in range(n):
swapped = False # optimize code, so it exits if now swaps on inner loop
# Inner traversal using j index
for j in range(n-i): # n-i as positions on right are in order in bubble
# Swap if the element KeyN is greater KeyN1
keyN = list[j].get(key)
keyN1 = list[j+1].get(key)
if keyN > keyN1:
swapped = True
list[j], list[j + 1] = list[j + 1], list[j] # single line swap
if not swapped: # if no swaps on inner pass, list is sorted
return # exit function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# list/dictionary sample
list_of_people = [
{"name": "Risa", "age": 18, "city": "New York"},
{"name": "John", "age": 63, "city": "Eugene"},
{"name": "Shekar", "age": 18, "city": "San Francisco"},
{"name": "Ryan", "age": 21, "city": "Los Angeles"}
]
# assuming uniform keys, pick 1st row as source of keys
key_row = list_of_people[0]
# print list as defined
print("Original")
print(list_of_people)
for key in key_row: # finds each key in the row
print(key)
bubbleSort(list_of_people, key) # sort list of people
print(list_of_people)