|
Overview | Covid19 RapidAPI | Jokes API | JWT Login | Database CRUD |
APIs in this Sub Menu
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are the front-end of the API. Java and API resource definitions are used for RESTful API definitions. Abstraction of Frontend and Backend code, the exchange of standard data format (JSON), and guidelines for exchange (REST) is a technique that saves a lot of time between developers. Learning APIs is a highly recommended step for every developer trying to break into the world of tech.
- Covid19: RapidAPI example. This is introducing APIs by accessing something that already exists. RapidAPI shows how many practice RESTful definitions. Almost any data source imagined can be accessed here.
- Jokes: An introduction to Java RESTful API libraries. A Java Database is used for the Data Model, providing data persistence. This example introduces concepts like JPA and POJOs.
- Database CRUD: A full RESTful API example. This data if properly managed in deployment and migrated when changed can last forever.
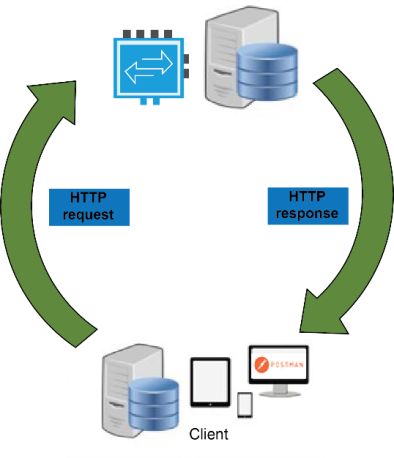
Web API Overview
A Web API is an application programming interface typically for a web browser. Non-changing or Static Endpoints are used in interacting with the server-side Web APIs. RESTful Web APIs use HTTP methods to access resources via URL parameters, and use JSON for transmitting text between client and server.
- Server. In these examples, we will be using Java to define REST APIs. Java tools have been around a long time and thus are popular for building RESTful APIs
- REST: Representational State Transfer. A set of guidelines on how to architect a network-connected software system.
- Client-server: One guideline is a client and server must be decoupled from each other, allowing each to develop independently.
- Layered system: The client may access the resources on the server indirectly through other layers such as a proxy or using authentication. This will be clarified by application and security requirements.
- Client. JavaScript is the frontend language used to consume data from the Python defined REST APIs. Fetch will be used to make HTTP requests, as well as handle HTTP response. There are four basic HTTP methods, they align with Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD).
- GET => Retrieve/Read data
- POST => Create data
- PUT => Update data
- DELETE => Delete data
- REST endpoints will have similarity from application to application. In planning APIs, for a Users system you can anticipate key methods. The Users RESTful APIs would likely contain these endpoints.
- GET: /users => Get a list of users
- GET: /users(id) => Get a single user
- POST: /users => Create a new user
- PUT: /users(id) => Update a user
- DELETE: /users(id) => Delete a user
- Once a RESTful API receives and processes an HTTP request, it will return an HTTP response. Included in this response is an HTTP status code. Common status codes are shown.
- 200 => OK, this response will then have the promise of JSON data
- 400 => Bad Request
- 404 => Not Found
- 500 => Internal Server Error (aka bug)