AWS Deployment Guide
Description of key methods process used to deploy a Spring/Java website; AWS EC2, Docker, docker-compose, and Nginx
- Deployment Overview
- Key/Values required as you go through these procedures
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Electric Cloud Compute (EC2) Setup
- Install packages
- Clone and Change Directory to project location
- Build the Web Service
- Create Dockerfile to run Web Service
- Create docker-compose file share Web Service
- Running Docker using docker-compose.yml
- Verifying Web Application via Docker commands
- Preparing the Docker Web Application for Internet Access
- Update Deployment
- FAQS for Problems
Deployment Overview
Deploying a Web Application enables a Server to serve the components of a Web Application to clients. Deployment is the tools and service used to enable the Web Application on the Internet. The process of can use many different cloud servers, as well as choice in tools and services.
- EC2: Amazon Web Services is a cloud computing platform that the PUSD district has provided for us to serve our Web Application.
- GitHub: At this point in time, we should be aware that we are using GitHub is an open platform to share our Web Application code on the Internet.
- Docker and docker-compose: To host a Web Application you need to prepare an environment that contains the Web Application code and all the dependencies (POM.xml for Java) Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications.
- Nginx: To find a Web Application on a server, there needs to be a process to listen for the Web request and direct it to the Web Application. Nginx is an open source software for web serving, reverse proxy, caching, load balancing, media streaming, and more.
- Certbot: Web traffic on internet is reliably served over Secure Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (https). Certbot is a free, open source software tool for automatically using Let’s Encrypt certifications
- DNS: Natively, the web works off of IP addresses. Domain Name Services (DNS) allows the assignment of a friendly name to our Web Server. This name is built into Nginx/Certbot configuration files. Freenom is the service used to register the nighthawkcodingsociety.com domain.
Key/Values required as you go through these procedures
Listed are Keys, you need to obtain Values. It is important that you recognize the sample Values as you work through these procedures, then replace them with the Values that are specific to your use case.
- GitHub HTTPS link:
- IAM user:
- EC2 name:
- EC2 Public IPs:
- DNS Name:
- DNS Subdomain name(s)
- Docker Port:
- docker-compose, proxy pass Port:
- docker-compose, docker Image:
- Nginx server file(s):
Amazon Web Services (AWS): Electric Cloud Compute (EC2) Setup
Preparing and AWS EC2 instance is the process of creating a cloud computer. This process starts by logging into your AWS IAM user, searching for EC2.
- To get started, launch a new AWS EC2 instance to learn process and understand how to work with Linux. here are some key considerations.
- Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI), the class will be using Ubuntu you should check on last verified version with a Teacher before proceeding
- When it comes to picking memory or disk it is VERY important to pick Free Tier. As stated, this will only be used for testing and then it will be disposed for cost efficiency.
- When presented with access dialog for http and https, make sure you check these boxes. Remember you are making a Web application that will run over http and https.
- Name the security group (.pem) file after your team. It may be necessary to use SSH to access your EC2 instance.
- The remainder of the steps you can use the defaults, refer to AWS documentation for guidance: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/EC2_GetStarted.html
- At the end of this process you need to “Connect to Instance”. This will provide you a terminal like experience.
Install packages
Terminal commands are shown, these commands will be run from Terminal after you connect to your EC2 name.
Update/Upgrade all packages on your EC2
$ sudo apt update; sudo apt upgrade
Install Java Runtime Environment
$ sudo apt install default-jre
$ java -version
Install Java Development Kit
$ sudo apt install default-jdk
$ javac -version
Maven is required to build project
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt upgrade
$ sudo apt install maven
$ mvn -version
Clone and Change Directory to project location
These commands move your Web Application code onto you EC2 cloud computer
$ cd
$ git clone https://github.com/nighthawkcoders/spring_portfolio.git
Build the Web Service
These steps will require you test Maven build prior to the final deployment process.
- Maven Build and Jar package command
$ cd ~/spring_portfolio $ ./mvnw package- If Maven fails, try this and repeat Maven command
$ sudo apt install -y dos2unix $ dos2unix ./mvnw $ chmod +x ./mvnw
- If Maven fails, try this and repeat Maven command
- Run Java Application
$ cd ~/spring_portfolio $ java -jar target/spring-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar - At this point we will type ctrl+c as we will now run a Docker File to do this step
Create Dockerfile to run Web Service
A Dockerfile is a configuration used to run the Web Service. This is placed in a file called Dockerfile. It is best to add this to VS Code and pull it, or you can update in place with nano, vi, or vim editor and use command line commands to push it into your repository. The Dockerfile should be considered Code!
- Edit the Dockerfile
$ nano Dockerfile - Insert the Dockerfile commands, note that they are similar to Bash commands performed earlier. Follow prompts on screen to save file when complete, look for Key/Value (GitHub HTTPS link) that requires change for your project.
# syntax=docker/dockerfile:1 FROM openjdk:16-alpine3.13 WORKDIR /app RUN apk update && apk upgrade && \ apk add --no-cache git maven COPY . /app RUN ./mvnw package CMD ["java", "-jar", "target/spring-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar"] # EXPOSE port that is defined in spring_portfolio.git application.properties EXPOSE 8085
Create docker-compose file share Web Service
A docker-compose file is a configuration used to share your Docker Web Service and resources with the Linux system. This file enable Linux to have access to the container and the persistent data application via the /volumes location.
Once again it is best to add the docker-compose.yml in VS Code and pull it. You can edit it on the machine itself using vi, vim, or nano.
- Edit docker-compose.yml
$ nano docker-compose.yml - Change the docker-compose.yml Keys/Values.
- ports 8085:nnnn - Left 8085 is port to be used on system, by curl and Nginx config.
- ports nnnn:8085 - Right 8085 is port exposed by Docker: EXPOSE 8085
- device /home/ubuntu/spring_portfolio/volumes - is my project defining a volumes directory for database and uploads outside of container
```yml
version: ‘3’
services:
web:
image: java_springv1
build: .
ports:
- “8085:8085” volumes:
- persistent_volume:/app/volumes volumes: persistent_volume: driver: local driver_opts: o: bind type: none device: /home/ubuntu/spring_portfolio/volumes ```
IF you cloned the repository after 9/8 you may have to change ports to 8085:8085
Running Docker using docker-compose.yml
At this point, it is best to review complete files on GitHub and for Docker and docker-compose: https://github.com/nighthawkcoders/spring_portfolio. Review the Key/Values mentioned in this document. Make sure your Docker and docker-compose files a personalized to your project.
- Make sure you are in project directory
$ cd ~/spring_portfolio/ - install docker-compose
$ sudo apt install docker-compose -y - Run docker-compose
$ sudo docker-compose up -d - Output from docker-compose. When running this command, docker-compose will run all the Docker steps and build a Web Application running in a Docker container, a virtual environment.
Creating network "spring_portfolio_default" with the default driver
Building web
Step 1/9 : FROM openjdk:16-alpine3.13
---> d0ce03c9330c
Step 2/9 : WORKDIR /app
.... LOTS of STEPs and OUTPUT ...
Successfully built 68d68ad9699b
Successfully tagged ava_springv1:latest
WARNING: Image for service web was built because it did not already exist. To rebuild this image you must use `docker-compose build` or `docker-compose up --build`.
Creating flask_portfolio_web_1 ... done
Verifying Web Application via Docker commands
Here is a look at some of the commands behind the scenes. None of these are required to get things working, but show the results of the Docker and docker-compose.yml files and commands.
- docker-compose ps The running Web process, “ps” is a linux command or option that provides information related to the processes on a system. Look at headings in relation to outputs of the docker-compose process.
ubuntu@ip-172-31-1-138:~/flask_portfolio$ docker-compose ps Name Command State Ports -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ava_springv1 gunicorn main:app Up 0.0.0.0:8085->8080/tcp,:::8085->8080/tcp - docker ps A more comprehensive list of all the docker processes on the system. In this process reports, many of the alternate projects running on this AWS server are show. The flask_portfolio_web_1 process is the items specific to this tutorial.
buntu@ip-172-31-1-138:~/flask_portfolio$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 749a93bc11ce flask_port_v1 "gunicorn main:app" 45 minutes ago Up 45 minutes 0.0.0.0:8086->8080/tcp, :::8086->8080/tcp flask_portfolio_web_1 89155782b853 java_springv1 "java -jar target/sp…" 6 days ago Up 6 days 0.0.0.0:8085->8080/tcp, :::8085->8080/tcp spring_portfolio_web_1 9415d6397d2e python_cspv1 "gunicorn main:app" 2 weeks ago Up 2 weeks 0.0.0.0:8082->8080/tcp, :::8082->8080/tcp nighthawk_csp_web_1 4bf324458bf6 python_laxv1 "gunicorn main:app" 5 weeks ago Up 5 weeks 0.0.0.0:8084->8080/tcp, :::8084->8080/tcp lax_web_1 7a6dff6425e9 python_ctev1 "gunicorn main:app" 5 weeks ago Up 5 weeks 0.0.0.0:8083->8080/tcp, :::8083->8080/tcp cte_web_1 abd77b8e77af java_csav2 "java -jar target/cs…" 5 weeks ago Up 5 weeks 0.0.0.0:8081->8080/tcp, :::8081->8080/tcp nighthawk_csa_web_1 - docker images This lists all of the docker images, or containers, that are used to serve the process shown above. The flask_port_v1 is the image created from the Docker file created in this tutorial. The image contains the running Web application.
ubuntu@ip-172-31-1-138:~/flask_portfolio$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE flask_port_v1 latest 68d68ad9699b 51 minutes ago 1.01GB java_springv1 latest e85a584b1836 6 days ago 523MB python_laxv1 latest 713c84a30d3b 5 weeks ago 1.16GB python_ctev1 latest 1608eaee06c7 5 weeks ago 1.18GB python_cspv1 latest b9bb27be863b 5 weeks ago 1.12GB java_csav2 latest 4055a9fd5ea7 5 weeks ago 570MB python 3.9 d0ce03c9330c 7 weeks ago 915MB alpine latest e66264b98777 8 weeks ago 5.53MB openjdk 16-alpine3.13 2aa8569968b8 17 months ago 324MB
Preparing the Docker Web Application for Internet Access
There are a couple of steps to this preparation. We need to direct the internet to the Server running the Web Application, this is done using Domain Name Service (DNS). After being directed to the Web Server, the server needs to respond to the Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP), this will be manged by Nginx. Additionally, we will be required to support Secure HTTP (HTTPS), a utility called Certbot will augment our Nginx configuration with a certificate.
DNS provider and setup
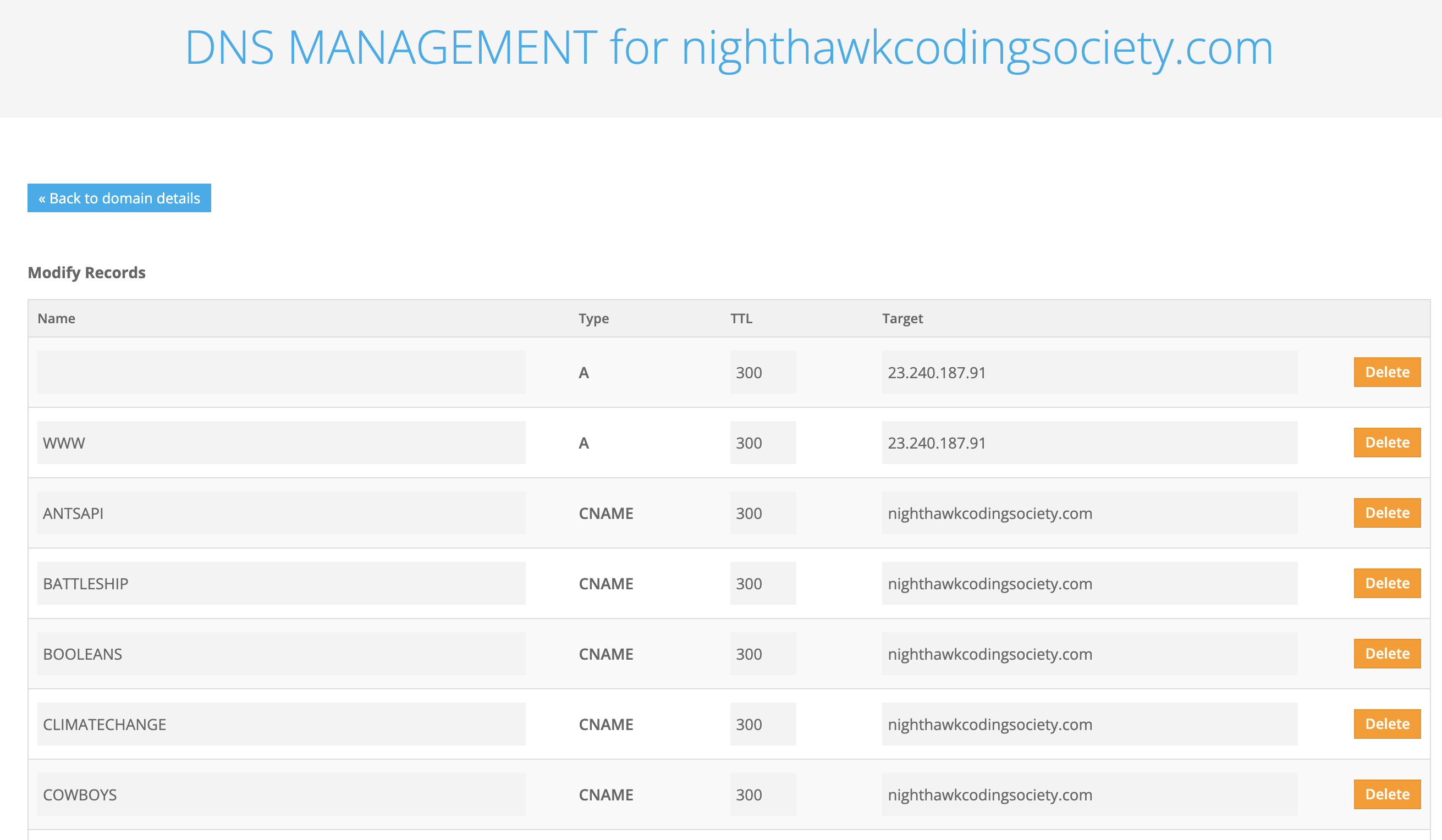
Each student scrum team is required to learn how to obtain a DNS provider and setup an independent domain. However, the final set up will be using a Subdomain under nighthawkcodingsociety.com.
A picture is included to show key elements in setting up a domain with a DNS provider. The nighthawkcodingsociety.com is using Freenom as its service provider. As you build your own DNS server you will need to obtain your own IP address and domain.
This illustration is dependent on…
- EC2 Public IPs: 3.233.212.71
- Docker Compose Port: 8085
- DNS Name: nighthawkcodingsociety.com
- DNS Subdomain name(s): battleship.nighthawkcodingsociety.com. cowboys.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
A minimum configuration will have the two “A” type definitions using you Public IP address. These two are resolved with a single Web Application. The “CNAME” type is used for subdomains, these will resolve to a different Web Application.
Nginx install, configuration, and services
Each student scrum team will perform Nginx installation and setup on an AWS EC2 test server. The final configuration will be on AWS server managed by Teachers or Student DevOps Engineers.
Enable Nginx to retrieve Java Web Application on internet request (Reverse Proxy)! Make a server file located at /etc/nginx/sites-available/nighthawk.
- Install Nginx on Ubuntu servers
$ sudo apt install nginx - Go to location of Nginx server configuration files
$ cd /etc/nginx/sites-available - Open editor to Create your own “Nginx server configuration”
$ nano nighthawk - Edit your own Nginx server configuration making modifications to primary server file (1 required):
- DNS Name(s): nighthawkcodingsociety.com www.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
- docker-compose, proxy pass Port: 8085
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name nighthawkcodingsociety.com www.nighthawkcodingsociety.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8085;
# Simple requests
if ($request_method ~* "(GET|POST)") {
add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Origin" *;
}
# Preflight requests
if ($request_method = OPTIONS ) {
add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Origin" *;
add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Methods" "GET, POST, OPTIONS, HEAD";
add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Headers" "Authorization, Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept";
return 200;
}
}
}
- Or, or in addition, edit your own Nginx server configuration making modifications to subdomain file (0 to many):
- DNS Name(s): spring.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
- docker-compose, proxy pass Port: 8085
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name spring.nighthawkcodingsociety.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8085;
# Simple requests
if ($request_method ~* "(GET|POST|PUT)") {
add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Origin" *;
}
# Preflight requests
if ($request_method = OPTIONS ) {
add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Origin" *;
add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Methods" "GET, POST, OPTIONS, PUT, HEAD";
add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Headers" "Authorization, Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept";
return 200;
}
}
}
- Activate/enabled Nginx server configuration:
- nginx configuration file: nighthawk
$ sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/nighthawk /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
$ sudo nginx -t
- If there are no errors, restart NGINX so the server is an endpoint to the internet:
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Testing HTTP endpoint
Before finishing, this is a good opportunity to test everything you have done.
- Direct Test of Web Application Endpoint. This should return HTML related to the home page of the Web site. If this fails, you need to review Docker and docker-compose configurations.
$ curl http://localhost:8085; - Testing unsecure HTTP endpoint on the internet. Go to a browser an type your DNS domain:
http://nighthawkcodingsociety.com.- Timeout. This means something is wrong with EC2 Public IP.
- Nginx Default page. This means DNS is working, but something is wrong with you Nginx configuration.
- Broken Gateway. This means Nginx is working, but something is wrong with Web Application endpoint on machine, if this fails something is wrong with Web Application. This requires you to look at Docker and docker-compose configuration.
Certbot install and configuration
Each student scrum team will learn Certbot on on AWS EC2 test server, establish working https web application. The final configuration will be on AWS server managed by Teachers or Student DevOps Engineers.
$ sudo snap install core; sudo snap refresh core
$ sudo snap install --classic certbot
$ sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
$ sudo certbot --nginx
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx
Which names would you like to activate HTTPS for?
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1: nighthawkcodingsociety.com
2: csa.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
3: csp.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
4: flm.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Select the appropriate numbers separated by commas and/or spaces, or leave input
blank to select all options shown (Enter 'c' to cancel):
Cert not yet due for renewal
You have an existing certificate that has exactly the same domains or certificate name you requested and isn't close to expiry.
(ref: /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/nighthawkcodingsociety.com-0001.conf)
What would you like to do?
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1: Attempt to reinstall this existing certificate
2: Renew & replace the cert (limit ~5 per 7 days)
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
Renewing an existing certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for nighthawkcodingsociety.com
http-01 challenge for csa.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
http-01 challenge for cso.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
http-01 challenge for flm.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
Waiting for verification...
Cleaning up challenges
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nighthawk_society
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nighthawk_csa
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nighthawk_csp
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nighthawk_flm
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration.
2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for
new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this
change by editing your web server's configuration.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
Traffic on port 80 already redirecting to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nighthawk_society
Traffic on port 80 already redirecting to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nighthawk_csa
Traffic on port 80 already redirecting to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nighthawk_csp
Traffic on port 80 already redirecting to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nighthawk_flm
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Your existing certificate has been successfully renewed, and the new certificate
has been installed.
The new certificate covers the following domains:
https://nighthawkcodingsociety.com,
https://csa.nighthawkcodingsociety.com,
https://csp.nighthawkcodingsociety.com, and
https://flm.nighthawkcodingsociety.com,
You should test your configuration at:
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=nighthawkcodingsociety.com
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=csa.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=csp.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=flm.nighthawkcodingsociety.com
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/nighthawkcodingsociety.com-0001/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/nighthawkcodingsociety.com-0001/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2022-03-06. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again
with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of
your certificates, run "certbot renew"
- If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
After this is complete, Let’s Encrypt can be set up to renew certificates if expring within 30 days. This is accomplished using cron jobs (periodic jobs). In this case, we will run the job daily which checks & updates the certificates
crontab -e # edit crontab file
0 12 * * * /usr/bin/certbot renew --quiet # add this line to the file (runs renew daily)
Update Deployment
This procedure is a very short, as much of the deployment performed is persistent on your EC2/Ubuntu.
Goto Project directory
Check your docker processes. Make sure git has nothing to commit.
$ cd ~/spring_portfolio/
$ docker-compose ps
Name Command State Ports
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
spring_portfolio_web_1 java -jar target/spring-0. ... Up 0.0.0.0:8085->8080/tcp,:::8085->8080/tcp
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
89155782b853 java_springv1 "java -jar target/sp…" 8 weeks ago Up 8 weeks 0.0.0.0:8085->8080/tcp, :::8085->8080/tcp spring_portfolio_web_1
$ git status
On branch master
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/master'.
nothing to commit, working tree clean
Shutdown process and update source
Stop docker processes and git pull
$ docker-compose kill Killing spring_portfolio_web_1 ... done
At this point your server is down, look at it from browser
502 Bad Gateway
Update code
ubuntu@ip-172-31-1-138:~/spring_portfolio$ git pull
remote: Enumerating objects: 11, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (11/11), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 6 (delta 2), reused 6 (delta 2), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (6/6), 562 bytes | 562.00 KiB/s, done.
From https://github.com/nighthawkcoders/spring_portfolio
c308ee0..c1f06f1 master -> origin/master
Updating c308ee0..c1f06f1
Fast-forward
src/main/resources/application.properties | 4 +++-
1 file changed, 3 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
Rebuild and Restart Web Application
Force rebuild of docker container. This will take several minutes.
- Note. There is extra opportunity here, for a better way, to do this by using cache and having github pull outside of container (volume?)
$ docker-compose build --no-cache # this will take several minutes
Building web
Step 1/7 : FROM openjdk:16-alpine3.13
---> 2aa8569968b8
Step 2/7 : WORKDIR /app
---> Running in 327ed1c61755
Removing intermediate container 327ed1c61755
---> 3769ad96350d
Step 3/7 : RUN apk update && apk upgrade && apk add --no-cache git
---> Running in 76646a4afae0
... Lots of Output ...
Downloaded from central: https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/codehaus/plexus/plexus-utils/3.2.1/plexus-utils-3.2.1.jar (262 kB at 246 kB/s)
Downloaded from central: https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/eclipse/sisu/org.eclipse.sisu.inject/0.3.4/org.eclipse.sisu.inject-0.3.4.jar (379 kB at 350 kB/s)
[INFO] Replacing main artifact with repackaged archive
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 30.843 s
[INFO] Finished at: 2022-09-11T19:44:18Z
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Removing intermediate container f5f06740c57a
---> 34e9da840534
Step 6/7 : CMD ["java", "-jar", "target/spring-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar"]
---> Running in 5f29b55a0fdc
Removing intermediate container 5f29b55a0fdc
---> e299d92bd2e6
Step 7/7 : EXPOSE 8080
---> Running in 12b33cccbf0e
Removing intermediate container 12b33cccbf0e
---> e5b2b8c5644d
Successfully built e5b2b8c5644d
Successfully tagged java_springv1:latest##
Run docker-compose
$ docker-compose up -d Recreating spring_portfolio_web_1 ... done
Now server is up, test in Browser for recent change
Java Home Page
Setting up automatic deployment
- This is how to do automatic deployment using GitHub actions, which can run code after a push is made.
- First, a secret will need to be set up from your AWS PEM file for your SSH key, in the Repository Settings > Secrets create a new secret called SSH_KEY
- This SSH_KEY should contain encoded output of your AWS PEM
base64 -w 0 aws_ssh_key.pem(this encodes the key to use base64 ASCII characters) - GitHub Actions can be specified in the .github/workflows directory. In your repository create a file called .github/workflows/deploy_project.yml with the following content (this decodes the base64 key, uses SSH to update deployment project and rebuild docker container)
name: Deploy to Server
on: [push]
jobs:
AWS-Deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- run: echo $\{\{ secrets.SSH_KEY \}\} | base64 -d > key.pem
- run: chmod 400 key.pem
- run: ssh -i key.pem -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no ubuntu@[your server ip/domain name] 'cd ~/[your git folder]; git pull; docker-compose down; docker-compose up -d --build'
FAQS for Problems
Setting up docker without sudo
- Run the following commands to create a docker group & add your user
sudo groupadd docker sudo usermod -aG docker $USER - May need to run the following commands if you previously used sudo (to giv3e yourself ownership of .docker)
sudo chown "$USER":"$USER" /home/"$USER"/.docker -R sudo chmod g+rwx "$HOME/.docker" -R - For more information refer here
Errors on docker-compose or curl
if “docker-compose” or “curl” are not working and you want to start over. This will clean up existing Docker container(s) and volume(s) and enable you to restart them.
- If any of these steps fail, try “sudo” prefix to elevate permissions.
- If commands are incomplete or something is missing, continue on. These commands are intended to cleanup Docker, missing means it is already cleaned up.
cd into your spring portfolio project
$ cd ~/project
stop docker-compose processes
$ docker-compose down # try sudo if it fails
Remove container
$ docker ps # list all containers $ docker rm -f container-name # try sudo if it fails
Remove volume
$ docker volume ls # list all volumes $ docker volume rm volume-name # try sudo if it fails
Restart the containers using the following command
$ docker-compose up -d # try sudo if it fails
Use curl to test
$ curl http://localhost:8085;