College Board Create Performance Task
30% of the student AP Test and a big portion of achievement in class is in building your own application. Start thinking about this now!
- Learning Create Performance Task, 30% of grade on AP exam
- Additional Resources
- Hacks
Learning Create Performance Task, 30% of grade on AP exam
Each time we engage in Code/Code/Coding it is an opportunity to think of the possibility of fulfilling the Create Performance Task requirement. But, this is a student project and responsibility is on you. To be thinking and preparing is a mindset, one that Del Norte CompSci Teachers advise as we proceed through topics. Thus, we are getting and early start by using this Pair Share project as an iteration through the entire process, as that is the foundational principle behind PBL.
Teacher will help as directed by College Board…
- Provide instruction, practice, and feedback related to content and skills that will help students succeed on the performance task. This can include, but needs not be limited to, the iterative development process, strategies for collaboration, the development of both data and procedural abstractions, and describing an algorithm’s purpose and explaining how it functions.
- Brainstorm problems that programming can address or brainstorm special interests that students want to incorporate when developing a program.
- Assist students in defining their focus and choice of topics without making selections for them (e.g., by asking questions).
- Review the performance task directions and provide multiple opportunities to practice and discuss the entire performance task and individual prompts of the task.
- Explain the role the teacher can and cannot play in providing students with assistance during the actual performance task; teachers should encourage students to take advantage of the opportunity to get assistance and feedback from teachers and peers during practice.
- Review the scoring guidelines with students to help them understand how their work will be assessed. Teachers should remind students that the scoring guidelines align to the prompts in the performance task, so they must respond to all the prompts in their attempt to obtain the highest score possible.
Disclaimer. Del Norte Computer Science Teachers are not experts in College Board scoring guidelines. It is best to look for examples of performance task submissions at high, medium, and low levels on College Board Web Site. Any grades you receive on any project in class may differ from scoring of the performance task by College Board.
General Requirements, from CB Exam Description
Prior to the official administration of the Create performance task, students need practice implementing programs that first include sequencing, then incorporate selection and iteration, and finally use procedures and lists. While collaboration on ideation and program design and development during the Create performance task is not required, it is encouraged.
You will be provided with a minimum of 12 hours of class time to complete and submit the following:
- Final program code (created independently or collaboratively)
- A video that displays the running of your program and demonstrates functionality you developed (created independently)
- Written responses to all the prompts in the performance task (created independently)
Del Norte Computer Science Principles Teachers are requiring students to do collaborative ideation, program design, prototyping and pair programming on these early activities that we grade in class.
Create Performance Task Skills and Rubric Breakdown (Out of 6 Points)
Note: There is no partial credit (0 or 1 point for each section). AP Computer Science Principles Exam is a through-course performance task that assesses Computational Thinking Practices 1, 2, 3, and 4 across six rubric rows.
Row 1: Program Purpose and Function
- Assesses students’ ability to explain how a code segment or program functions. (Skill: Code Analysis)
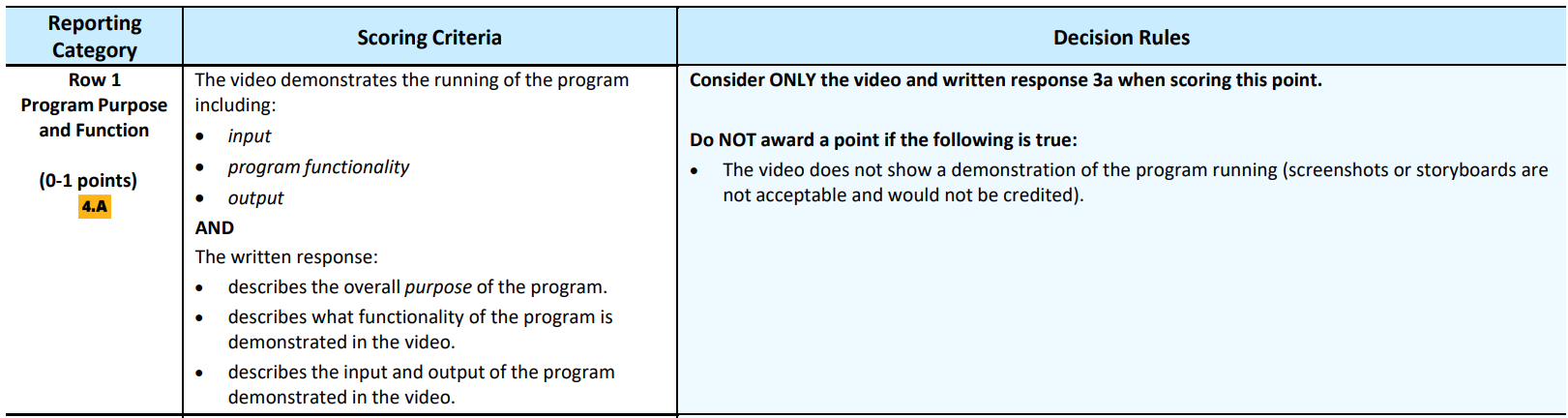
- For 3a, make sure to differentiate between program purpose and function
- They are defined in the scoring guidelines
Row 2: Data Abstraction
- Assesses students’ ability to use abstraction to manage complexity in a program. (Skill Abstraction in Program Development - data)
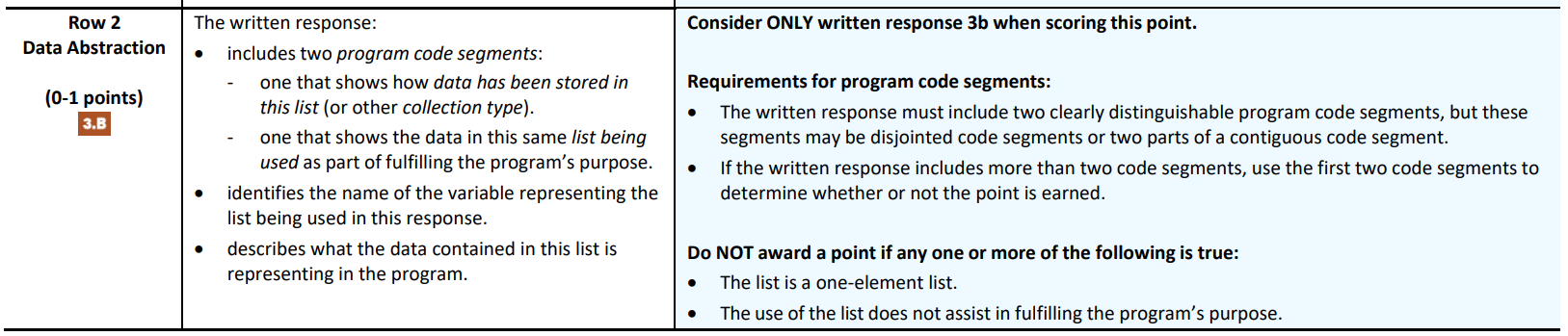
Row 3: Managing Complexity
- Assesses students’ ability to explain how abstraction manages complexity. (Skill Abstraction in Program Development explain complexity)
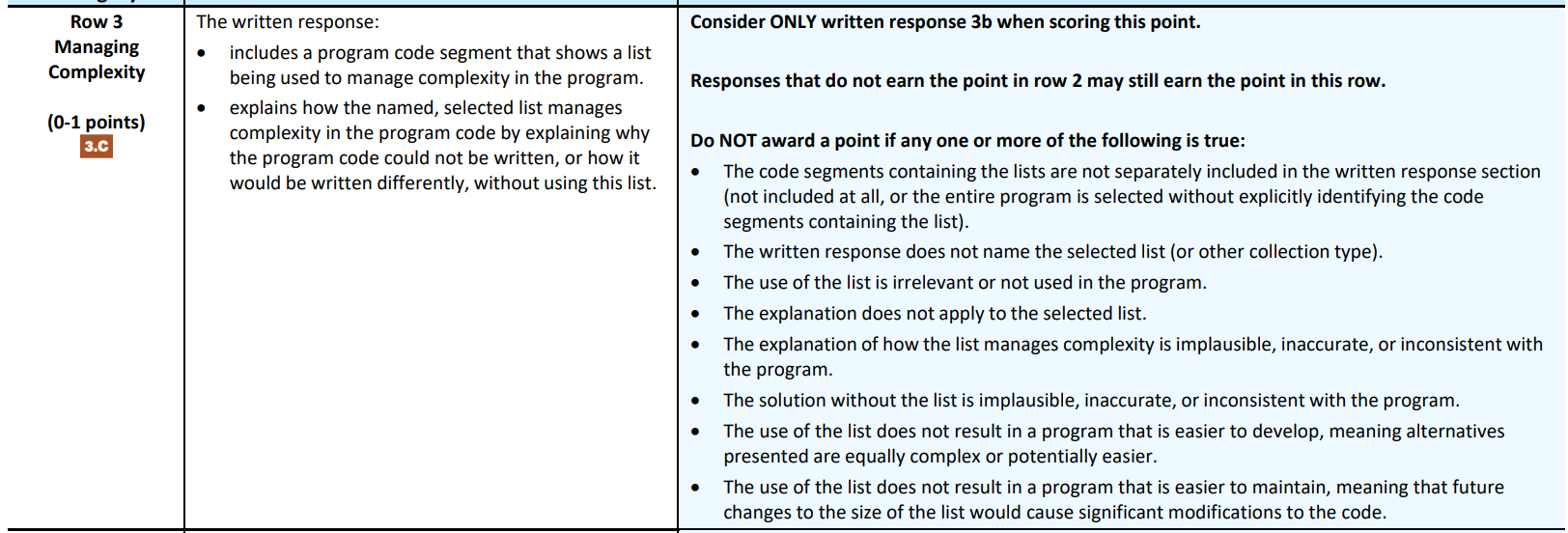
- Be specific about how the program manages complexity in the context of your own program
Row 4: Procedural Abstraction
- Assesses students’ ability to use abstraction to manage complexity in a program. (Skill Abstraction in Program Development - procedures/functions)
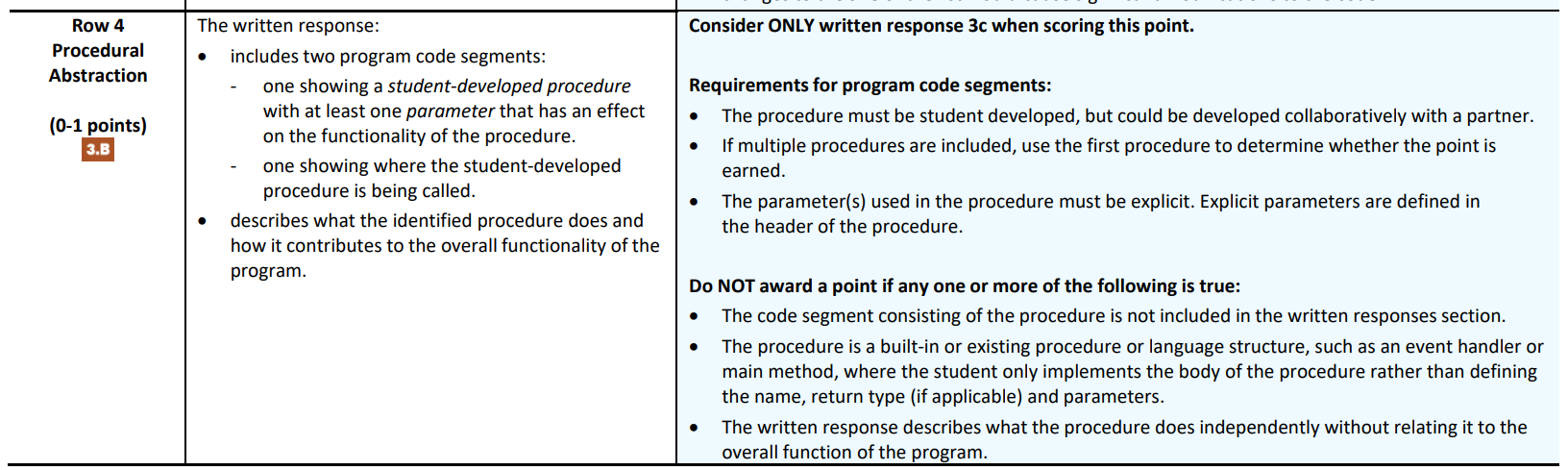
- Must be a student-developed procedure
Row 5: Algorithm Implementation
- Assesses students’ ability to implement and apply an algorithm. (Skill Algorithms and Program Development)
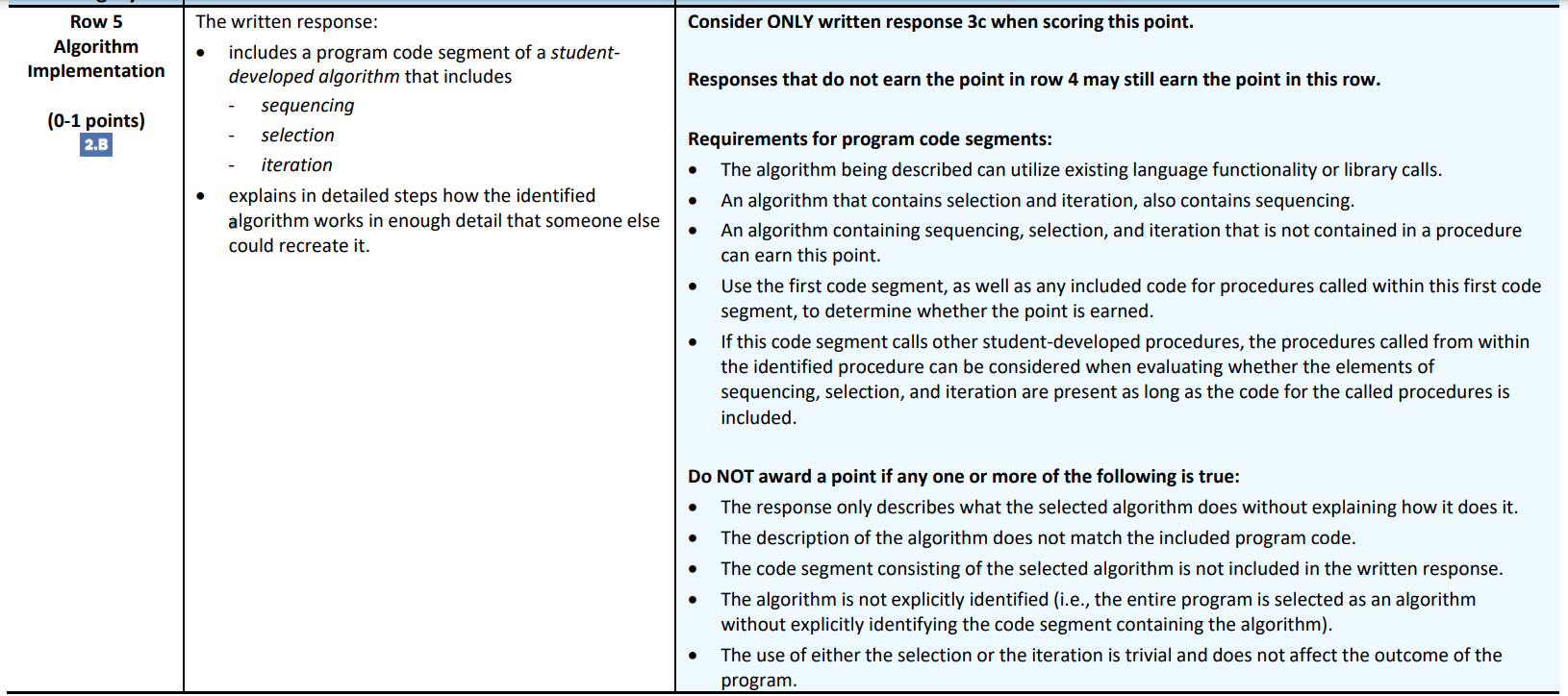
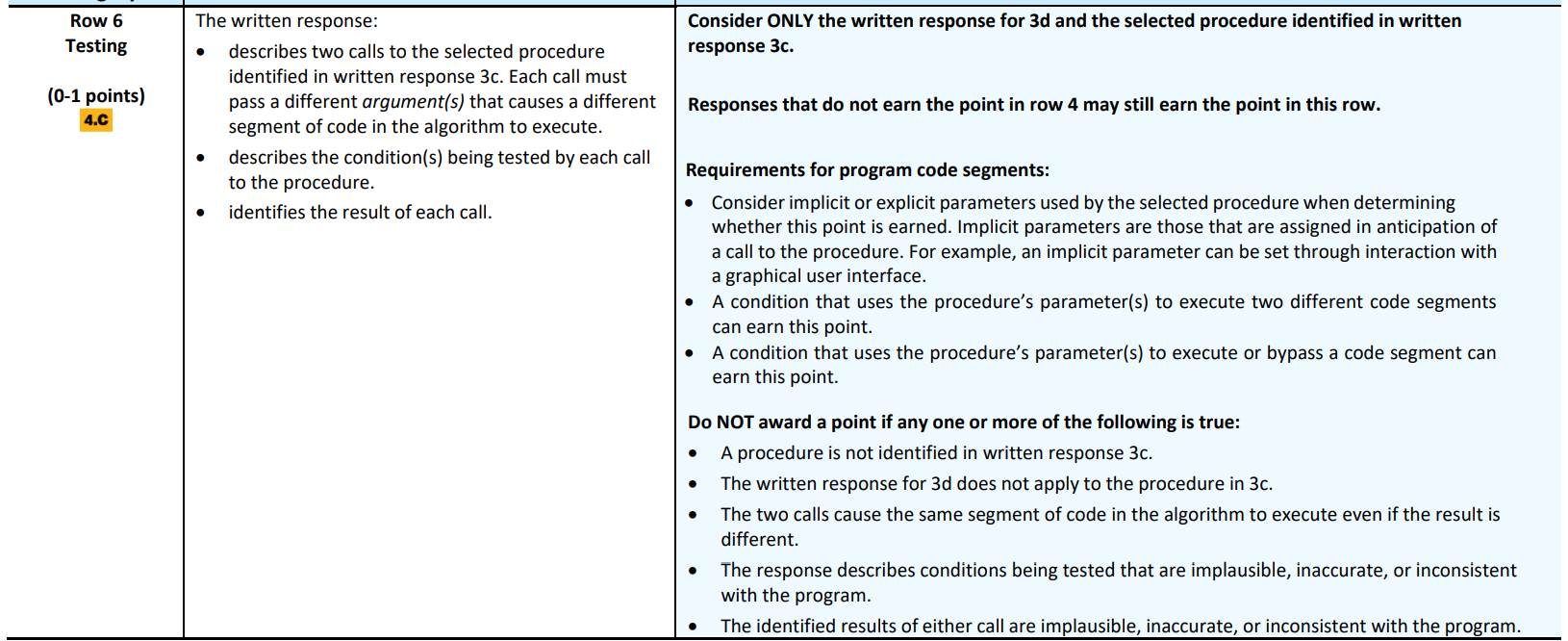
Row 6: Testing
- Assesses students’ ability to investigate the situation, context,or task. (Skill Computational Solution Design - testing)
Collaboration Rules, from CB Q&A
Collaboration happens when two or more students are actively engaged in the development of a program. Some examples of acceptable ways to collaborate are as follows.
- 2 students who are writing the entire program together, perhaps using pair programming.
- 2 or more students who have divided a larger, more complex program into different separate parts, each writing their own part and then assembling the pieces into the finished program.
- Student(s) giving feedback on an independently or collaboratively written program.
- Student(s) providing debugging assistance to another student or collaborative group of students.
Del Norte Computer Science Principles Teachers want to see all of these prescribe methods of collaboration utilized.
Collaboration without Plagiarism, from CB Q&A
If students are combining independently written program code with another student, they should cite that the program code is written by a collaborative peer. To protect the anonymity of the collaborative peer, students simply state that the portion of program code was written by their collaborative peer, rather than putting the names of themselves or their collaborative peer in the program code.
When completing the Create performance task, students will need to add substantial revisions and additional functionality when starting with preexisting program code. Simply changing an image in a game or the names of variables is insufficient.
Del Norte Computer Science Principles Teachers have zero tolerance for plagiarism. Misrepresenting your own work and not attending class (without makeup) are the only ways to get less than 70% in the class. Plagiarism is 0%, being in class is 50%, any individual effort with attendance gets 70%. The biggest jeopardy to getting a bad grade in the class is getting a 0%, the only possibility of such is plagiarism or missing class without makeup.
Additional Resources
-
2021 Scoring Guidelines and Scored Create Task Examples
- Please note, these scoring guidelines were for 2021. Please check the CollegeBoard website in case there is an updated version.
-
AP Computer Science Principles Course and Exam Description
- Create Performance Task Verbs Explanation (pg 175 of Course/Exam Description)
- The CollegeBoard AP Computer Science Principles Course includes videos scoring Create Task Examples
- CollegeBoard’s Tips on the Create Task
Hacks
Start an outline on how you will prepare for the Create Performance Task project.
- Review How I got a 5, by Bria
- Establish a personal or pair Scrum Board with active and future Issues
- Start a design that _post that can be reviewed to see if it meets the basicCreate Performance Task requirements. Be sure to pick something that you don’t burn out on or is not overly common.