Binary Logic and Abstraction
Taking a look at binary abstractions (ASCII, Unicode, Images),logic gates, etc
- Binary, Data, Data Structures, Data Abstraction (ASCII, Unicode, Color Codes),
- Math in Binary
- ASCII and Unicode
- Color Codes
- Logic Gates
- Unsigned Addition
- Signed Addition
- Technical helpers
- Hacks
Binary, Data, Data Structures, Data Abstraction (ASCII, Unicode, Color Codes),
Algorithms, Data and Data Structures go together. It is required to have a data topic as you venture into Algorithms and Lessons. This blog is a collection of binary, data and data structures that should be your data topic!!! Use a data topic as you learn algorithms and programming.
- Explore that topic in Computer Science manner (research, jupyter notebooks, frontend / backend coding)
- Build a lesson that is more interesting, by explaining an algorithm and logic using a data topic.
- Teach with examples… Segment from CS50 and go to minute 13:15.
- Tour the Code. Use Binary Frontend Code to get you started. Better clone APCSP project drag and drop _posts/2022-07-07-PBL-binary.md to your project and Debug
- This Tech Talk will finish by reviewing hacks, the remainder of this blog and Binary Frontend Code is part of your research.
Math in Binary
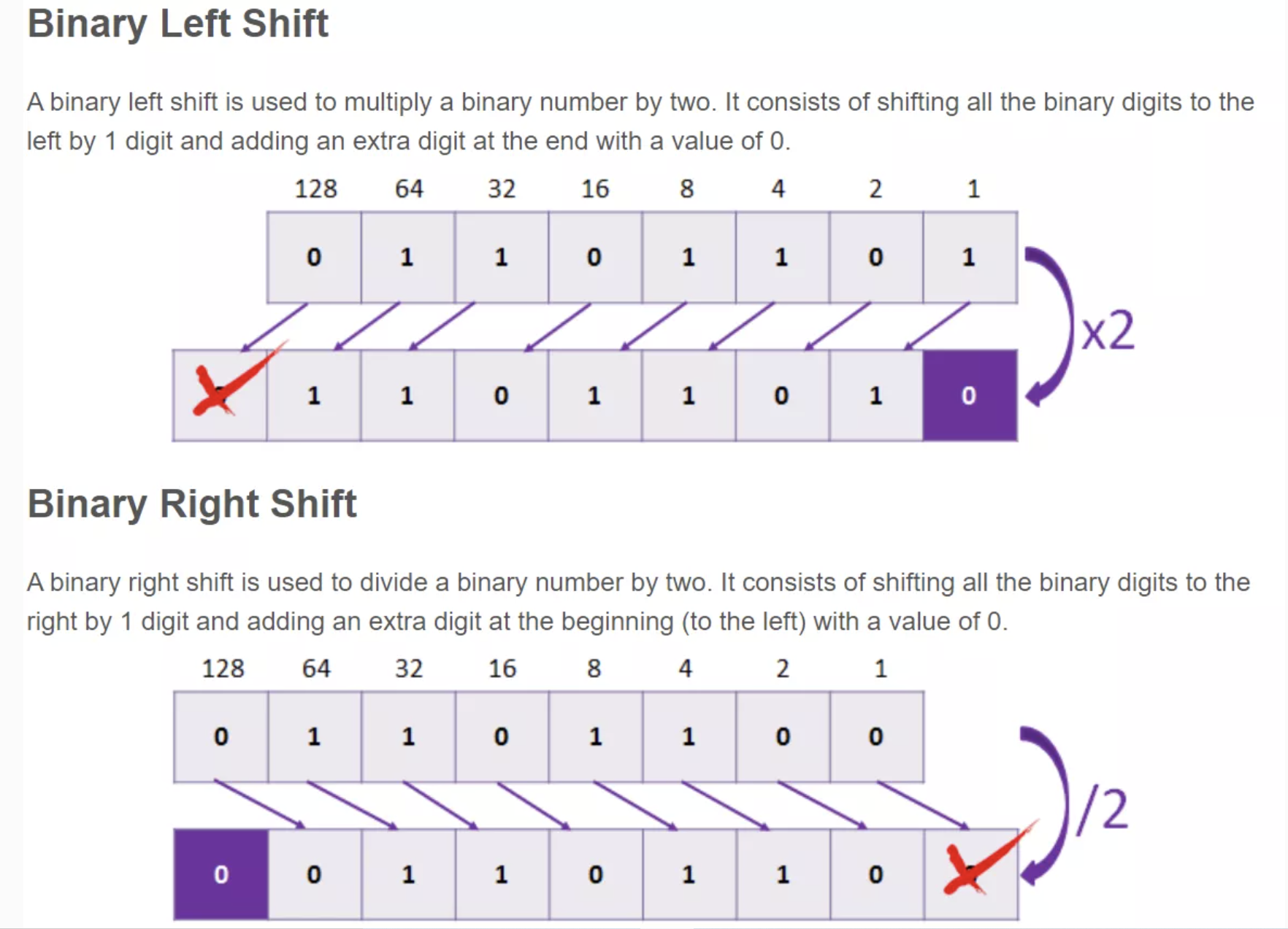
Learn binary by bitwise operators and more. Shifting bits is a common computer operation and does wonderful things in math like multiply and divide. Last bit always determines odd or even. Look for shift on w3schools
Logic of Shift
Explore right and left shifts with binary numbers.
- In an arithmetic shift, the bits that are shifted out of either end are discarded.
- In a left arithmetic shift, zeros are shifted in on the right.
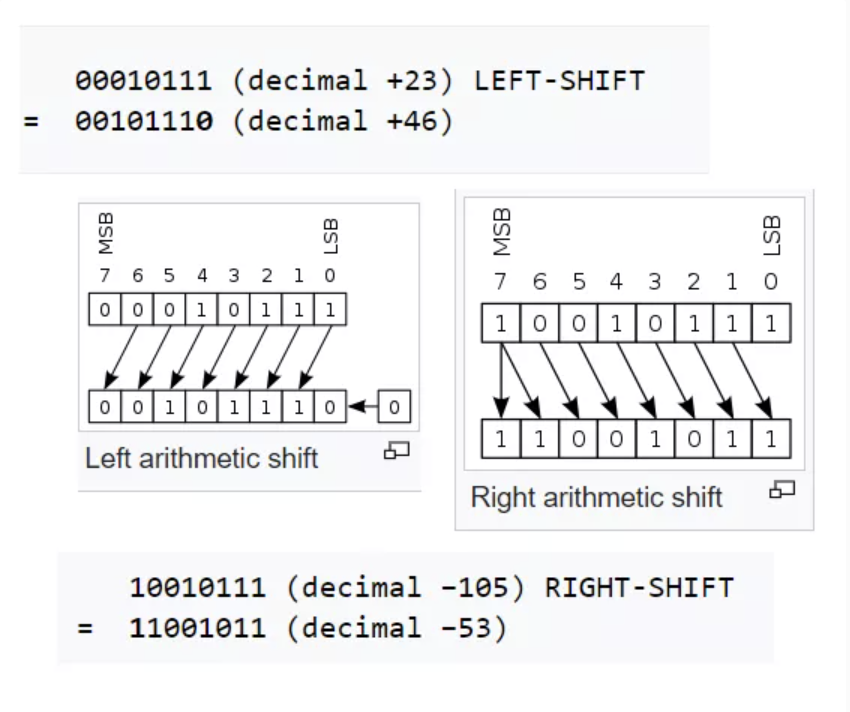
Understand binary Numbers by elaboration of Shift (2^^0, 2^^1, 2^^2)
How does the Power of 2 work? What is a binary number? What is Base2, Base10, Base16.
- This example uses an 8-bit register. Math can be represented in much in many more bits, 32 bits or 2 bytes is common for integer in modern computer languages.
- Most Significant Bit (MSB), least (LSB)
- This example shows negative and positive numbers, using technique called Twos Complement.
- In the first case, the leftmost digit was shifted past the end of the register, and a new 0 was shifted into the rightmost position. Positive Multiply.
- In the second case, the rightmost 1 was shifted out, and a new 1 was copied into the leftmost position, preserving the sign of the number. Negative Divide, this example obviously needs more study.
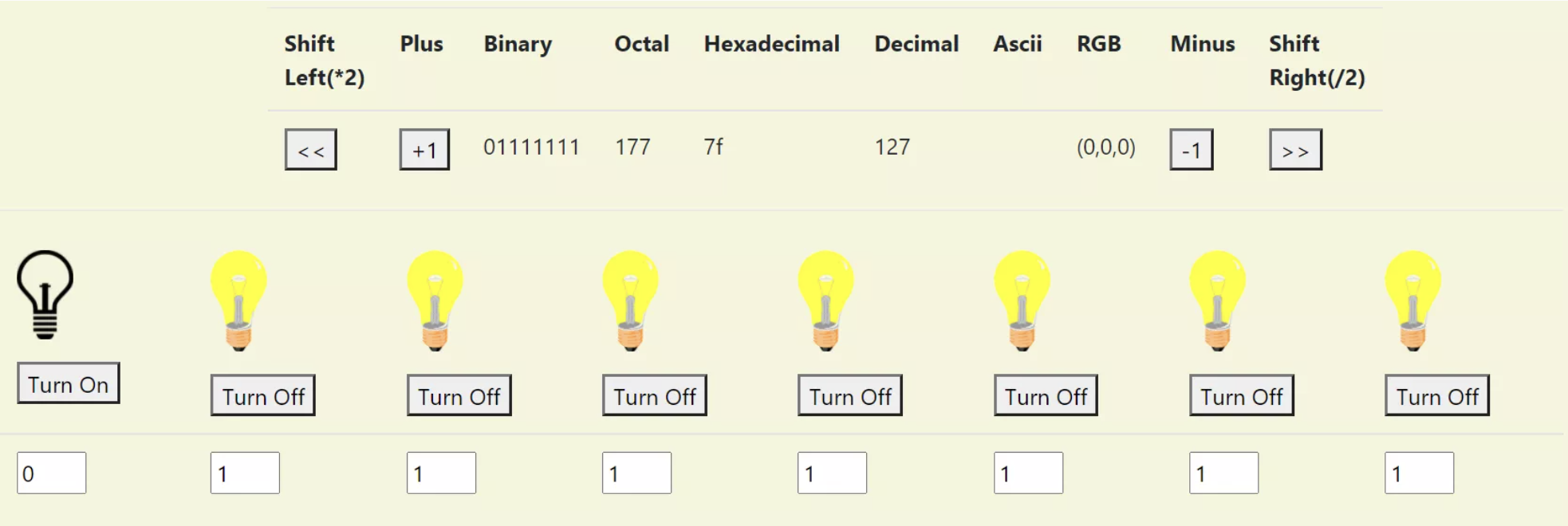
UI Concept/Design
Conceptualize on a UI that will illustrate binary and decimal. In learning these concepts, it is best to code and example to illustrate what is happening.
- n Right Shifts (divides by 2^n); n Left Shifts (multiplies by 2^n)
- Add buttons for “«” and “ »”
ASCII and Unicode
Computers represent more than Math. Mostly everyone is familiar with the characters on a keyboard and Emojis. These are all represented in binary, the data abstraction being the characters we visualize. 😂
Character Data Abstraction
How are characters stored? How many bits do they take?
- ASCII is 8 bits, it generally represent keys on keyboard. Look up ASCII Table.
- Unicode can be UTF-8, 16 or 32, each representing bits. ASCII is preserved in Unicode.
- ASCII - 7 bits, extended to 8 bits with Unicode
- UTF-8
- UTF-16
- UTF-32
Sample of Unicode characters.
UI Concept/Design
The ASCII value in picture should be change based off of the bits in evaluation you are doing. Bits displayed, label, and evaluation would be specific to evaluation type:
Original ASCII
Color Codes
Pixels are little dots on Monitors and TVs that make up the display. Each pixel has an Red Green and Blue value (RGB). All pictures we see or take are composed of RGB using a density measurement. These are stored and then represented by digitally or in print.
- Monitors
- 1280 x 1024 Super-eXtended Graphics Array (SXGA)
- 1366 x 768 High Definition (HD)
- 1600 x 900 High Definition Plus (HD+)
- 1920 x 1080 Full High Definition (FHD)
- 1920 x 1200 Wide Ultra Extended Graphics Array (WUXGA)
- TVs
- 4K Ultra HD: The term 4K means the screen is about 4,000 pixels wide. …
- 1080p (Full HD): This resolution is 1,920 x 1,080 pixels. …
- 720p (HD Ready): This is mostly found on smaller TVs, and it has a resolution of 1,280 x 720.
- Camera |Sensor Resolution (megapixels)|Typical Image Resolution (pixels)| |2.16|1800 x 1200| |3.9|2272 x 1704| |5.0|2592 x 1944| |7.1|3072 x 2304| |8.0|3264 x 2448| |10.0|3648 x 2736| |12.1|4000 x 3000| |14.7|4416 x 3312| |21.0|5616 x 3744|
A Color code is a 24 bit abstraction.
There are 8 bits for Red, 8 bits for Blue, and 8 bits for Green.
| Name | Hex Code | RGB Code |
| Black | #000000 | rgb(0, 0, 0) |
| Red | #FF0000 | rgb(255, 0, 0) |
| Maroon | #800000 | rgb(128, 0, 0) |
| Yellow | #FFFF00 | rgb(255, 255, 0) |
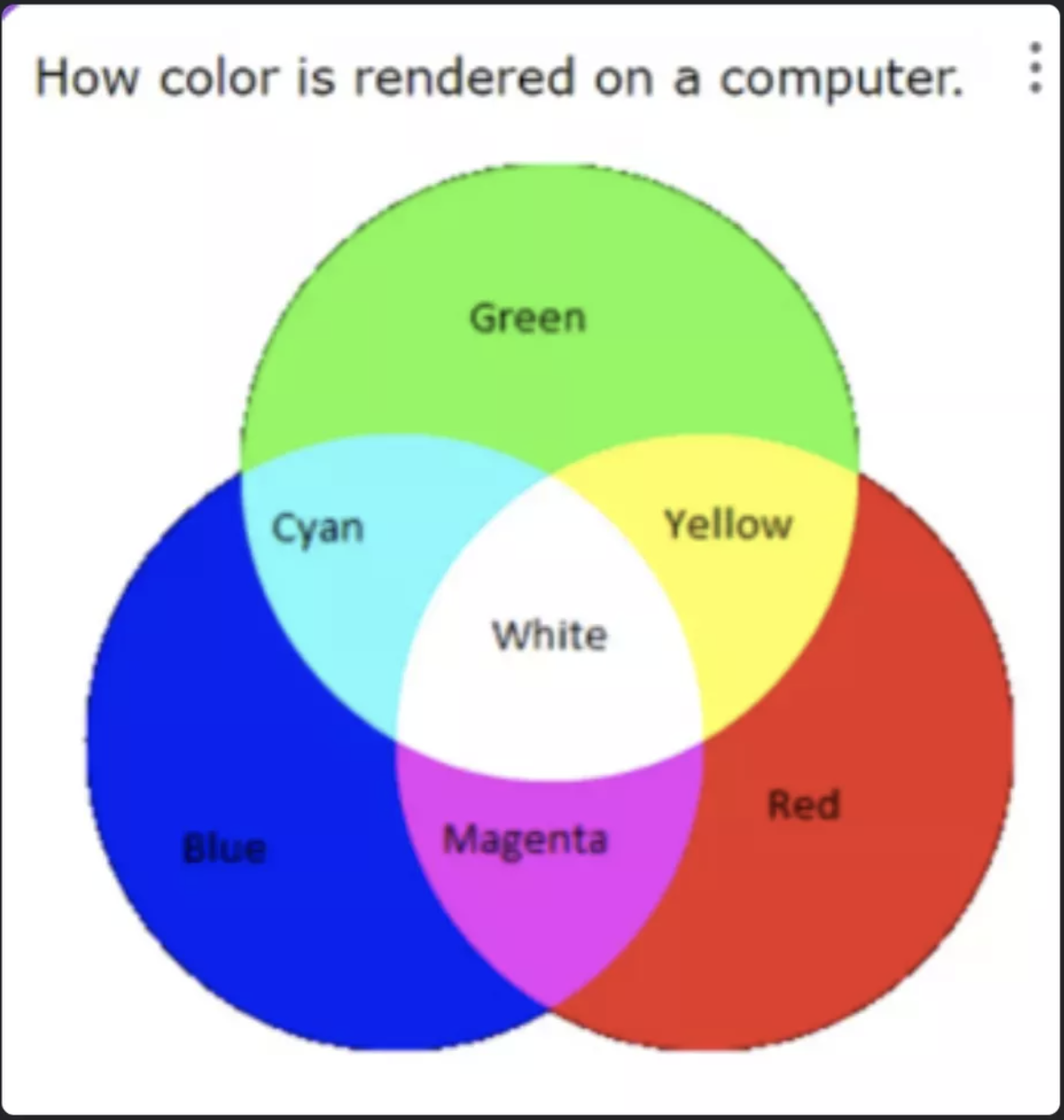 255 * 255 * 255 combinations of R, G, B
255 * 255 * 255 combinations of R, G, B
UI Design
Here is a sample program a student used to visualize color by turning buttons on and off.
by Anthony Vo 3 rows representing R, G, B Resulting color displayed in block
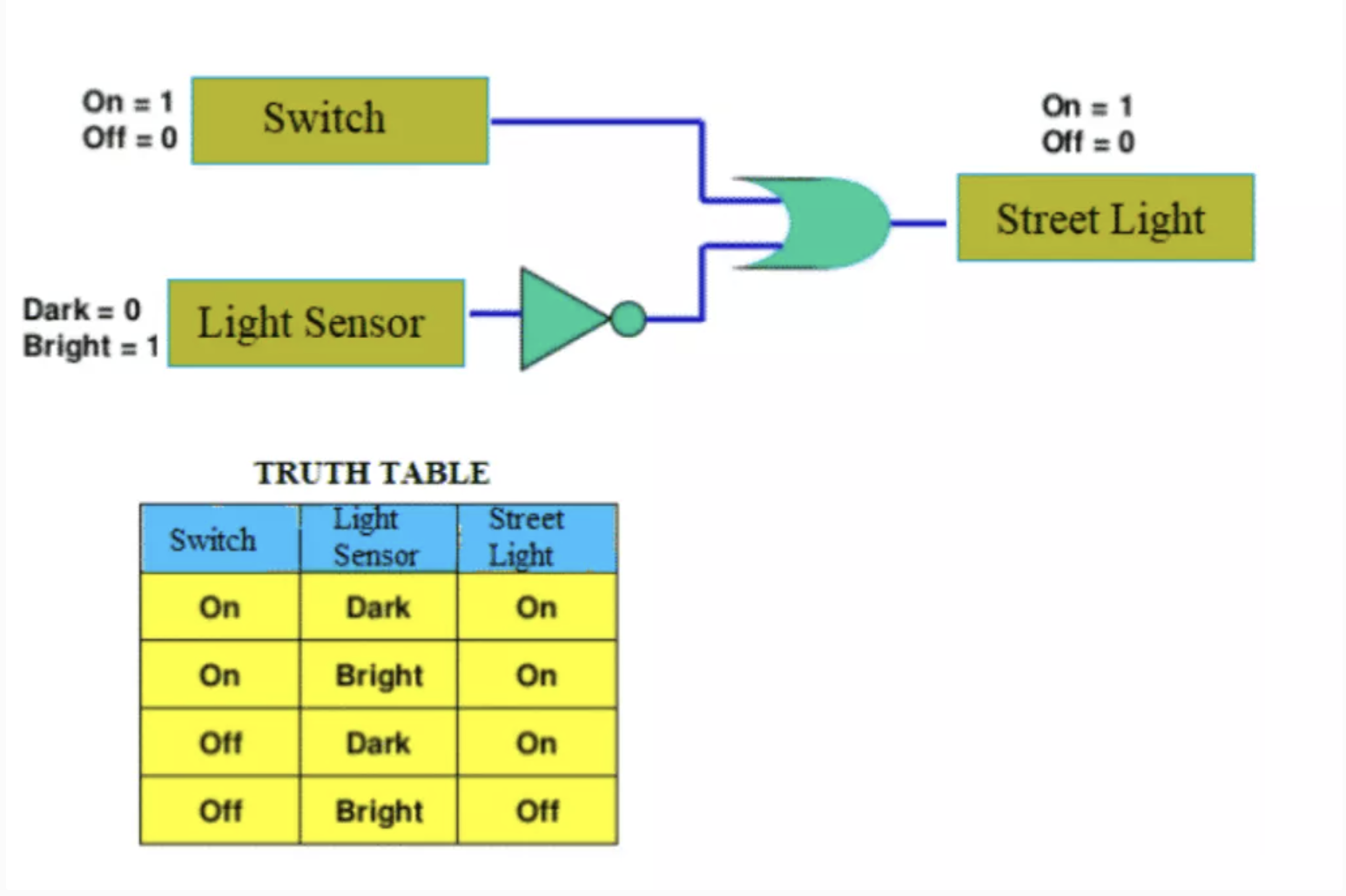
Logic Gates
The fundamentals of all decisions in computers is made by logic gates. These gates are visualized by permuting 1 and 0 across many different types of decisions. The result is an expression that evaluated to 1 or 0. These are called Truth Tables.
Logic Gates can be simulated with 2 bits
Look for bitwise operators on w3schools
UI Concept
Visual concept of logic gates
- Establish check boxes for A / B on and off
- Show result of Boolean Expression using Gate visual
Logic Gates
UI Design
Logic gate lab in JavaScript
by Kylie Scharf AB checkboxes with Submit button Table with Symbol, Description, and Result
Logic of Logic Gates
A logic gate can have two inputs (a,b) and by how changing these inputs it impacts the output(c).
- There are four possible inputs:
- 0 0
- 0 1
- 1 0
- 1 1
- Understanding the output enables us to understand a logical expressions. All outputs are routed in Logic Gates (similar to how a language is routed in Latin).
- AND is true for 1 1; NAND is true opposite of AND 0 0, 0 1, 1 0
- OR is true for 1 1, 0 1, 1 0, NOR is true opposite of OR 0 0
- XOR is true for 0 1, 1 0
Practical Application
Logic gates are used everywhere
Unsigned Addition
Here we are requesting 3 rows of bits to simulate Math. This could be done with 4, 8, or 16 bits.
Initial UI Implementation
 Action buttons for +1 and -1
Additional actions for Turn On and Turn Off
Action buttons for +1 and -1
Additional actions for Turn On and Turn Off
Unsigned Addition
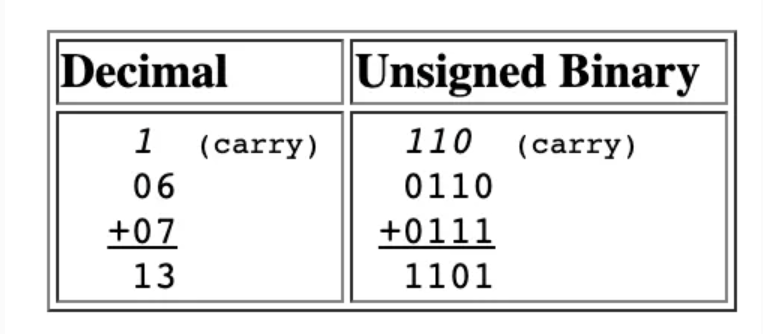
Signed Addition
Integers in most languages are int8, int16, int32, or int64. They typically reserve left most bit for sign.
Common concept for Integer Math
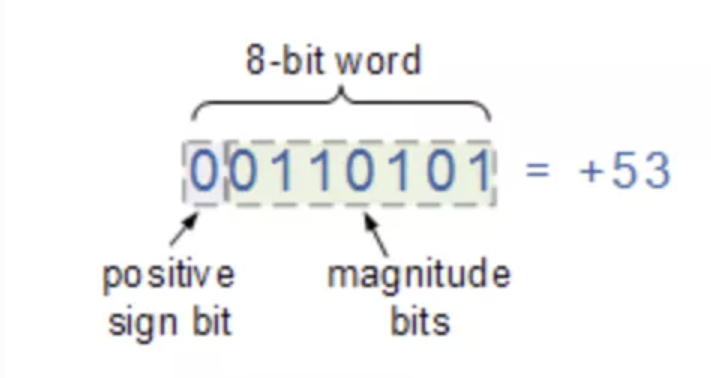 Positive number
Positive number
Basic concept, but not typically used
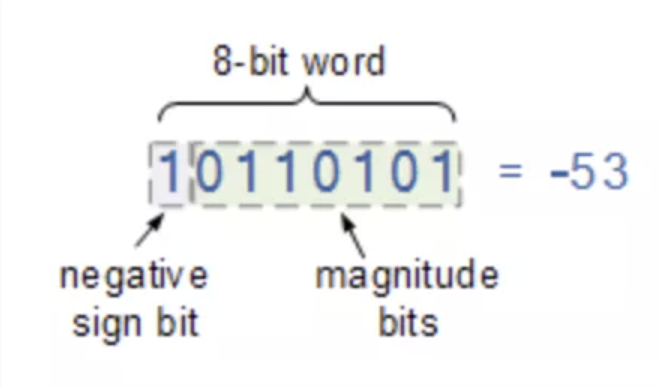 Negative number
Negative number
Inverting numbers, twos complement
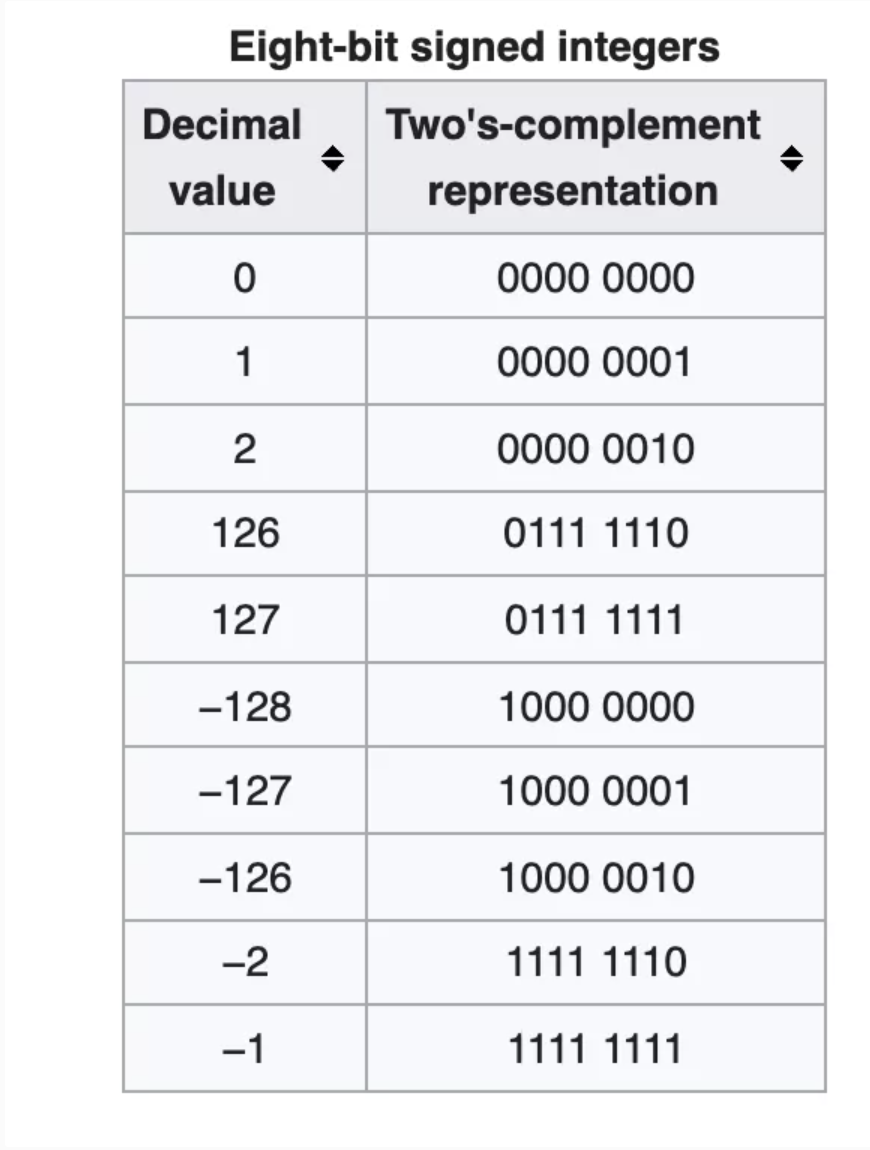 Two’s complement allows adding for signed and unsigned numbers
Two’s complement allows adding for signed and unsigned numbers
Basic concept is to invert/negate bits to produce negative. This allows numbers to be added together for expected results. » and »> have been adapted to handle signed and zero filled shifting.
Technical helpers
Harvard CS50 minute 0 to minute 50 to provide background on some of the information below.
Algorithm in Jinja2 to limit Bits per row
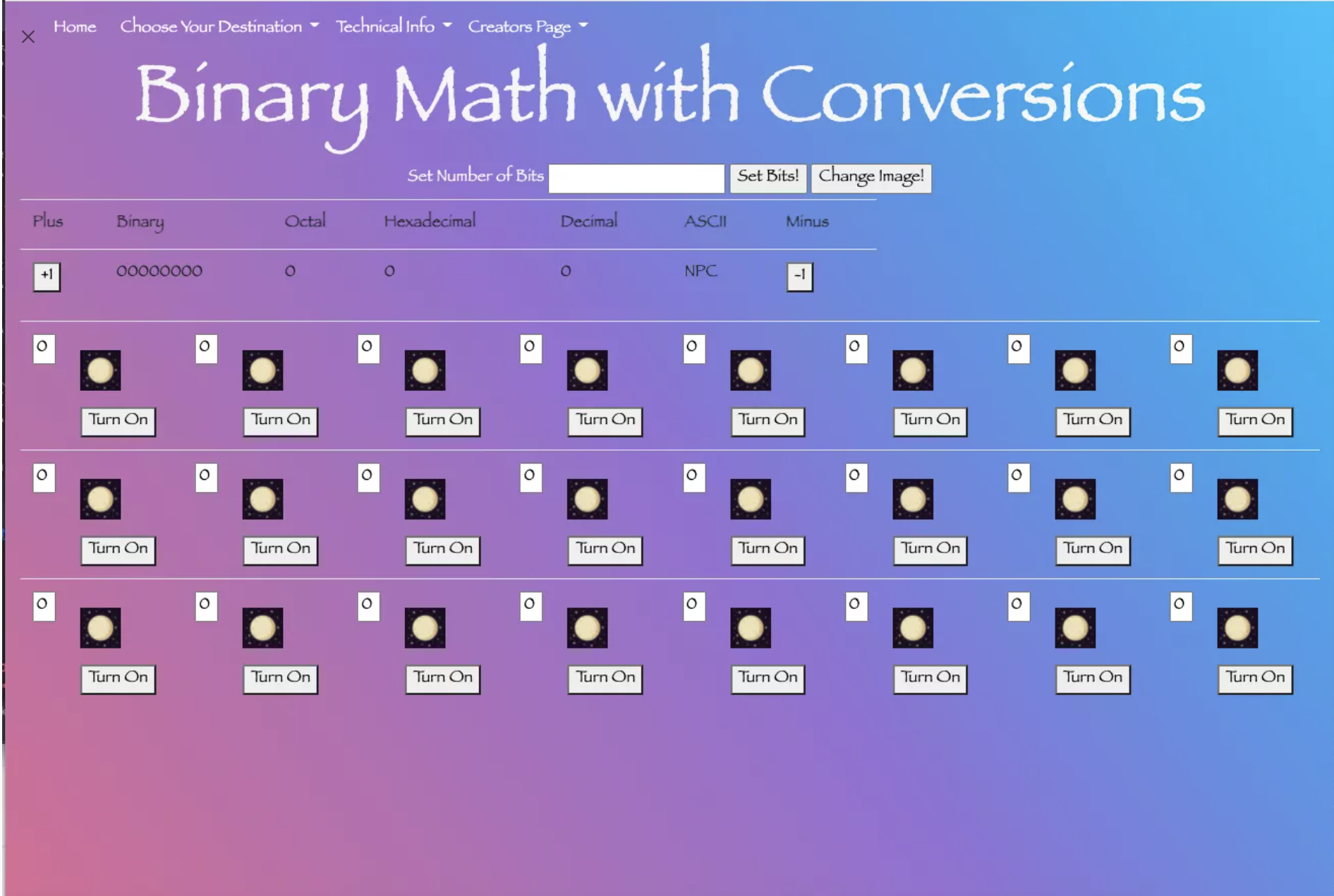 8 images per row by Kylie Scharf
Modulo 8 algorithm add <tr> for every eight bits (code).
8 images per row by Kylie Scharf
Modulo 8 algorithm add <tr> for every eight bits (code).
Research Helpers
CHAPTER 8 - Binary Addition and Two’s Complement Overview find by Val Wilson
Hacks
Data, Data Structures, and Algorithms work together. Data helps supply an interests/topic to an algorithm. It will be expected that you have a topic as you go through various algorithms.
- Use data abstraction (ie data structures) in your lesson
- Make sure you teach/learn elements from this blog as you learn algorithms
- Add “Science” into your process (research, jupyter notebook, and ultimately running application)
- Topics used in teaching, not listed in lesson/labs/homework need to be approved by Teacher. The topics above focus on data ideas from Unit 2 of AP Classroom.